A super-spreader of COVID-19 in Ningbo city in China
- PMID: 32554034
- PMCID: PMC7275998
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jiph.2020.05.023
A super-spreader of COVID-19 in Ningbo city in China
Abstract
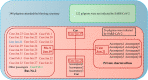
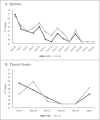
An outbreak of Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) has spread rapidly. It is imperative to control the epidemic by understanding the epidemiological feature, preventative quarantine, and effective hygiene measures. In the present study, we report a case of super-spreader who transmitted the disease to over twenty-eight persons in Ningbo, Zhejiang. Identifying and isolated super-spreaders, understanding the reasons behind the efficient transmission ability are important for the control and management of the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic.
Keywords: COVID19; Super-spreader; Virus features.
Copyright © 2020 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- World Health Organization . 2020. Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) situation reports.https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019/situatio...
-
- Chen Y., Wang A.H., Bo Yi, Ding K.Q., Wang A.H.B., Wang J.M. The epidemiological characteristics of infection in close contacts of COVID-19 in Ningbo city. Chin J Epidemiol. 2020:41. [In Chinese] - PubMed
-
- Corman V., Bleicker T., Brünink S., Landt O., Kaiser M., Molencamp R. World Health Organization; Geneva: 2020. Diagnostic detection of Wuhan coronavirus 2019 by real-time RT-PCR.https://www.who.int/-v1991527e5122341d99287a1b17c111902.pdf [Accessed 27 January 2020]. (January 13)
-
- National Health Commission. Up to 24:00 on 18 February, the latest situation of new coronavirus pneumonia, http://www.nhc.gov.cn/yjb/s7860/202002/8f2cfd17f4c040d89c69a4b29e99748c.... [Accessed 29 February 2020].
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

