Modified Anesthesia Protocol for Electroconvulsive Therapy Permits Reduction in Aerosol-Generating Bag-Mask Ventilation during the COVID-19 Pandemic
- PMID: 32554959
- PMCID: PMC7483857
- DOI: 10.1159/000509113
Modified Anesthesia Protocol for Electroconvulsive Therapy Permits Reduction in Aerosol-Generating Bag-Mask Ventilation during the COVID-19 Pandemic
Abstract
Introduction: Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) is a critical procedure in psychiatric treatment, but as typically delivered involves the use of bag-mask ventilation (BMV), which during the COVID-19 pandemic exposes patients and treatment staff to potentially infectious aerosols.
Objective: To demonstrate the utility of a modified anesthesia protocol for ECT utilizing preoxygenation by facemask and withholding the use of BMV for only those patients who desaturate during the apneic period.
Methods: This chart review study analyzes patients who were treated with ECT using both the traditional and modified anesthesia protocols.
Results: A total of 106 patients were analyzed, of whom 51 (48.1%) required BMV using the new protocol. Of clinical factors, only patient BMI was significantly associated with the requirement for BMV. Mean seizure duration reduced from 52.0 ± 22.4 to 46.6 ± 17.1 s, but seizure duration was adequate in all cases. No acute physical, respiratory, or psychiatric complications occurred during treatment.
Conclusions: A modified anesthesia protocol reduces the use of BMV by more than 50%, while retaining adequate seizure duration.
Keywords: COVID-19; Cohort studies; Electroconvulsive therapy; General anesthesia; Mechanical ventilation.
© 2020 S. Karger AG, Basel.
Figures
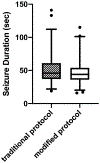
References
-
- Sackeim HA. Modern Electroconvulsive Therapy: Vastly Improved yet Greatly Underused. JAMA Psychiatry. 2017. August 1;74(8):779–80. - PubMed
-
- Munk-Olsen T, Laursen TM, Videbech P, Mortensen PB, Rosenberg R. All-cause mortality among recipients of electroconvulsive therapy: Register-based cohort study. Br J Psychiatry. 2007. May;190(5):435–9. - PubMed
-
- Mirzakhani H, Guchelaar H-J, Welch CA, Cusin C, Doran ME, MacDonald TO, et al. Minimum Effective Doses of Succinylcholine and Rocuronium During Electroconvulsive Therapy: A Prospective, Randomized, Crossover Trial. Anesth Analg. 2016;123(3):587–96. - PubMed
-
- Bryson EO, Aloysi AS, Farber KG, Kellner CH. Individualized Anesthetic Management for Patients Undergoing Electroconvulsive Therapy: A Review of Current Practice. Anesth Analg. 2017. June; 124(6): 1943–56. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

