Total knee revision arthroplasty: comparison between tibial tubercle osteotomy and quadriceps snip approach. Complication rate
- PMID: 32555089
- PMCID: PMC7944827
- DOI: 10.23750/abm.v91i4-S.9705
Total knee revision arthroplasty: comparison between tibial tubercle osteotomy and quadriceps snip approach. Complication rate
Abstract
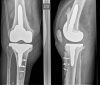
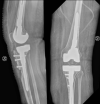
Background and aim of the work: The total knee arthroplasty (TKA) revision is not a second time of primary implant surgery but is a very complex issue for orthopedic surgeon. When local conditions make necessary a greater visualization, medial para-patellar access with quadriceps snip (QS) or the osteotomy of the tibial tuberosity (TTO) can be the solutions. This work aims to compare the quadriceps snip and the detachment of the tibial tubercle, focusing on possible complications.
Materials and methods: At our institution, between January 2017 and February 2019 52 TKA revision for periprosthetic joint infection (PJI) or aseptic mobilization were performed. In 43 cases an extensive surgical approach was required: for patients with range of movement (ROM) < 60° was chosen TTO, while with ROM > 60° a QS was performed. Clinical and radiological follow-up was available for all the 43 cases.
Results: The data about clinical outcome in our study show that both groups have a positive trend in KSS score over time with similar ROM results. Two partial avulsions of patellar tendon during revision surgery were reported. Clinical outcome in both groups has shown good results at the end of follow-up with no post-operative incidence of complications.
Conclusion: We can assert that both QS and TTO are good approach for TKA revision. Future studies will be needed to understand if preparatory ROM is a good way to decide which surgical approach to use.(www.actabiomedica.it).
Conflict of interest statement
Each author declares that he or she has no commercial associations (e.g. consultancies, stock ownership, equity interest, patent/licensing arrangement etc.) that might pose a conflict of interest in connection with the submitted article
Figures
References
-
- Registro Italiano ArtroProtesi - Annual Report. 2018, Istituto Superirore di Sanità
-
- Fehring T.K, et al. Early failures in total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2001;(392):315–8. - PubMed
-
- Delanois R.E, et al. Current Epidemiology of Revision Total Knee Arthroplasty in the United States. J Arthroplasty. 2017;32(9):2663–2668. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials