Bone marrow adipose tissue is a unique adipose subtype with distinct roles in glucose homeostasis
- PMID: 32555194
- PMCID: PMC7303125
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-020-16878-2
Bone marrow adipose tissue is a unique adipose subtype with distinct roles in glucose homeostasis
Abstract
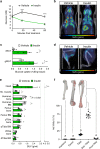
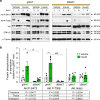
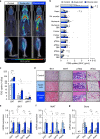
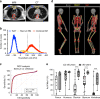
Bone marrow adipose tissue (BMAT) comprises >10% of total adipose mass, yet unlike white or brown adipose tissues (WAT or BAT) its metabolic functions remain unclear. Herein, we address this critical gap in knowledge. Our transcriptomic analyses revealed that BMAT is distinct from WAT and BAT, with altered glucose metabolism and decreased insulin responsiveness. We therefore tested these functions in mice and humans using positron emission tomography-computed tomography (PET/CT) with 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose. This revealed that BMAT resists insulin- and cold-stimulated glucose uptake, while further in vivo studies showed that, compared to WAT, BMAT resists insulin-stimulated Akt phosphorylation. Thus, BMAT is functionally distinct from WAT and BAT. However, in humans basal glucose uptake in BMAT is greater than in axial bones or subcutaneous WAT and can be greater than that in skeletal muscle, underscoring the potential of BMAT to influence systemic glucose homeostasis. These PET/CT studies characterise BMAT function in vivo, establish new methods for BMAT analysis, and identify BMAT as a distinct, major adipose tissue subtype.
Conflict of interest statement
E.J.R.v.B. has received the research support from the Siemens Healthineers and is the owner of QCTIS Ltd. Remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Comment in
-
Bone marrow adipose tissue function - is space a constraint?Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2020 Oct;16(10):543-544. doi: 10.1038/s41574-020-0400-6. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2020. PMID: 32778749 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Cinti S. Adipose organ development and remodeling. Compr. Physiol. 2018;8:1357–1431. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- FS/14/78/31020/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- R24 DK092759/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- FS/17/51/33096/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- RE/13/3/30183/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- RG/16/10/32375/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- K99 DE024178/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- SCAF/17/02/CSO_/Chief Scientist Office/United Kingdom
- PCL/17/04/CSO_/Chief Scientist Office/United Kingdom
- MR/M021394/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- P30 DK020572/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- MR/K010271/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- P30 DK089503/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

