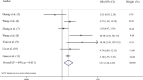
Type 2 diabetes as a major risk factor for COVID-19 severity: a meta-analysis
- PMID: 32555985
- PMCID: PMC10522215
- DOI: 10.20945/2359-3997000000256
Type 2 diabetes as a major risk factor for COVID-19 severity: a meta-analysis
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure: no potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures
Comment in
-
Severity of COVID-19 and diabetes mellitus: there is still a lot to be learned.Arch Endocrinol Metab. 2020 May-Jun;64(3):195-196. doi: 10.20945/2359-3997000000261. Arch Endocrinol Metab. 2020. PMID: 32555983 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
COVID-19 and diabetes: No time to drag our feet during an untimely pandemic.J Diabetes Complications. 2020 Sep;34(9):107621. doi: 10.1016/j.jdiacomp.2020.107621. Epub 2020 May 15. J Diabetes Complications. 2020. PMID: 33051004 No abstract available.
-
COVID 19: Diabetes and Obesity API-ICP Recommendations.J Assoc Physicians India. 2020 May;68(5):42-44. J Assoc Physicians India. 2020. PMID: 32610865
-
Does obstructive sleep apnea lead to increased risk of COVID-19 infection and severity?J Clin Sleep Med. 2020 Aug 15;16(8):1425-1426. doi: 10.5664/jcsm.8596. J Clin Sleep Med. 2020. PMID: 32441246 Free PMC article.
-
Are patients with rheumatologic diseases on chronic immunosuppressive therapy at lower risk of developing severe symptoms when infected with COVID-19?Clin Rheumatol. 2020 Jul;39(7):2067-2068. doi: 10.1007/s10067-020-05184-3. Epub 2020 May 30. Clin Rheumatol. 2020. PMID: 32474884 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
-
Cardiovascular complications in COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis.J Infect. 2020 Aug;81(2):e139-e141. doi: 10.1016/j.jinf.2020.05.068. Epub 2020 Jun 3. J Infect. 2020. PMID: 32504747 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Management of diabetes in patients with COVID-19 - Authors' reply.Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2020 Aug;8(8):669-670. doi: 10.1016/S2213-8587(20)30223-0. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2020. PMID: 32707113 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Risk Factors Associated with Mortality among Patients with COVID-19: Analysis of a Cohort of 1213 Patients in a Tertiary Healthcare Center.J Clin Med. 2022 May 14;11(10):2780. doi: 10.3390/jcm11102780. J Clin Med. 2022. PMID: 35628907 Free PMC article.
-
COVID-19 Triage and Test Center: Safety, Feasibility, and Outcomes of Low-Threshold Testing.J Clin Med. 2020 Oct 7;9(10):3217. doi: 10.3390/jcm9103217. J Clin Med. 2020. PMID: 33036445 Free PMC article.
-
Identifying the Quality Nuggets Amid the Explosion of COVID-19-Related Scientific Communication: An Insurmountable Challenge?J Clin Med Res. 2020 Oct;12(10):683-685. doi: 10.14740/jocmr4328. Epub 2020 Sep 21. J Clin Med Res. 2020. PMID: 33029277 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Severity of COVID-19 and diabetes mellitus: there is still a lot to be learned.Arch Endocrinol Metab. 2020 May-Jun;64(3):195-196. doi: 10.20945/2359-3997000000261. Arch Endocrinol Metab. 2020. PMID: 32555983 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Yang JK, Feng Y, Yuan MY, Yuan SY, Fu HJ, Wu BY, et al. Plasma glucose levels and diabetes are independent predictors for mortality and morbidity in patients with SARS. Diabet Med. 2006;23(6):623-8. - PubMed
-
- Harries A, Takarinda KC. F1000 Prime recommendation of Characteristics of and Important Lessons From the Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Outbreak in China: Summary of a Report of 72 314 Cases From the Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention. F1000 - Post-Publication Peer Review of the Biomedical Literature 2020. Available from: 10.3410/f.737420993.793572382. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical