Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography with compressed sensing at 1.5 T: clinical application for the evaluation of branch duct IPMN of the pancreas
- PMID: 32556465
- PMCID: PMC7554004
- DOI: 10.1007/s00330-020-06996-2
Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography with compressed sensing at 1.5 T: clinical application for the evaluation of branch duct IPMN of the pancreas
Abstract
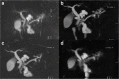
Objectives: To evaluate magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography (MRCP) with compressed sensing (CS) for the assessment of branch duct intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm (BD-IPMN) of the pancreas. For this purpose, conventional navigator-triggered (NT) sampling perfection with application-optimized contrast using different flip angle evolutions (SPACE) MRCP was compared with various CS-SPACE-MRCP sequences in a clinical setting.
Methods: A total of 41 patients (14 male, 27 female, mean age 68 years) underwent 1.5-T MRCP for the evaluation of BD-IPMN. The MRCP protocol consisted of the following sequences: conventional NT-SPACE-MRCP, CS-SPACE-MRCP with long (BHL, 17 s) and short single breath-hold (BHS, 8 s), and NT-CS-SPACE-MRCP. Two board-certified radiologists evaluated image quality, duct sharpness, duct visualization, lesion conspicuity, confidence, and communication with the main pancreatic duct in consensus using a 5-point scale (1-5), with higher scores indicating better quality/delineation/confidence. Maximum intensity projection reconstructions and originally acquired data were used for evaluation. Wilcoxon signed-rank test was used to compare the intra-individual difference between sequences.
Results: BHS-CS-SPACE-MRCP had the highest scores for image quality (3.85 ± 0.79), duct sharpness (3.81 ± 1.05), and duct visualization (3.81 ± 1.01). There was a significant difference compared with NT-CS-SPACE-MRCP (p < 0.05) but no significant difference to the standard NT-SPACE-MRCP (p > 0.05). Concerning diagnostic quality, BHS-CS-SPACE-MRCP had the highest scores in lesion conspicuity (3.95 ± 0.92), confidence (4.12 ± 1.08), and communication (3.8 ± 1.06), significantly higher compared with NT-SPACE-MRCP, BHL-SPACE-MRCP, and NT-CS-SPACE-MRCP (p = <0.05).
Conclusions: MRCP with CS 3D SPACE for the evaluation of BD-IPMN at 1.5 T provides the best results using a short breath-hold sequence. This approach is feasible and an excellent alternative to standard NT 3D MRCP sequences.
Key points: • 1.5-T MRCP with compressed sensing for the evaluation of branch duct IPMN is a feasible method. • Short breath-hold sequences provide the best results for this purpose.
Keywords: Magnetic resonance imaging; Pancreas; Pancreatic intraductal neoplasms.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors of this manuscript declare relationships with the following companies: Siemens Healthineers.
Figures


References
-
- Anupindi SA, Victoria T (2008) Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography: techniques and applications. Magn Reson Imaging Clin N Am 16:453–466 v - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

