Effects of transcranial direct current stimulation of left and right inferior frontal gyrus on creative divergent thinking are moderated by changes in inhibition control
- PMID: 32556475
- PMCID: PMC7321900
- DOI: 10.1007/s00429-020-02081-y
Effects of transcranial direct current stimulation of left and right inferior frontal gyrus on creative divergent thinking are moderated by changes in inhibition control
Erratum in
-
Correction to: Effects of transcranial direct current stimulation of left and right inferior frontal gyrus on creative divergent thinking are moderated by changes in inhibition control.Brain Struct Funct. 2020 Sep;225(7):2299. doi: 10.1007/s00429-020-02110-w. Brain Struct Funct. 2020. PMID: 32705345 Free PMC article.
Abstract
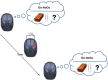
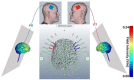
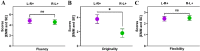
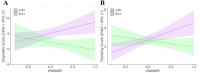
Divergent thinking (DT) as one component of creativity is the ability to search for multiple solutions to a single problem and is reliably tested with the Alternative Uses Task (AUT). DT depends on activity in the inferior frontal gyrus (IFG), a prefrontal region that has also been associated with inhibitory control (IC). Experimentally manipulating IC through transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) led to alterations in DT. Here, we aimed at further examining such potential mediating effects of IC on DT (measured as flexibility, fluency, and originality in the AUT) by modulating IC tDCS. Participants received either cathodal tDCS (c-tDCS) of the left IFG coupled with anodal tDCS (a-tDCS) of the right IFG (L-R + ; N = 19), or the opposite treatment (L + R-; N = 21). We hypothesized that L + R- stimulation would enhance IC assessed with the Go NoGo task (GNGT), and that facilitated IC would result in lower creativity scores. The reversed stimulation arrangement (i.e., L- R +) should result in higher creativity scores. We found that tDCS only affected the originality component of the AUT but not flexibility or fluency. We also found no effects on IC, and thus, the mediation effect of IC could not be confirmed. However, we observed a moderation effect: inhibition of left and facilitation of right IFG (L-R +) resulted in enhanced flexibility and originality scores, only when IC performance was also improved. We conclude that inducing a right-to-left gradient in IFG activity by tDCS is efficient in enhancing DT, but only under conditions where tDCS is sufficient to alter IC performance as well.
Keywords: AUT (alternative uses task); Creativity; Divergent thinking (DT); Flexibility; Fluency; IFG; Originality; tDCS.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Aron AR, Robbins TW, Poldrack RA. Inhibition and the right inferior frontal cortex: one decade on. Trends Cogn Sci. 2014;18:177–185. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

