Association between HDL-C levels and menopause: a meta-analysis
- PMID: 32557344
- PMCID: PMC7889539
- DOI: 10.1007/s42000-020-00216-8
Association between HDL-C levels and menopause: a meta-analysis
Abstract
Purpose: Menopause modifies women's lipid profiles. However, the fact that it is still unclear whether high-density lipoprotein-cholesterol (HDL-C) levels decrease in postmenopausal women necessitated a systematic review and meta-analysis.
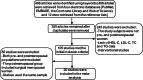
Methods: The PubMed, EMBASE, Cochrane Library, and Web of Science databases were searched and 498 articles published between 1987 and 2020 were retrieved. Studies reporting HDL-C, low-density lipoprotein-cholesterol (LDL-C), total cholesterol (TC), and triglyceride (TG) levels in both postmenopausal and premenopausal populations were included. The quality of the included studies was assessed using the Cross-Sectional/Prevalence Study Quality tool. The standard mean difference (SMD) and 95% confidence interval (CI) were estimated using random effects models. A meta-regression analysis and subgroup analysis were performed to identify potential modifiers. Egger's test and funnel plots were constructed to evaluate publication biases.
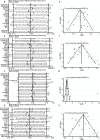
Results: Lipid profiles from 18 cross-sectional studies and two cohort studies including 5652 postmenopausal women and 7825 premenopausal women were meta-analyzed. HDL-C levels were not significantly different between the postmenopausal and premenopausal women (SMD = - 0.053, 95% CI - 0.171 to 0.066, p = 0.383) and were not affected by country, publication year, study quality in the meta-regression analysis, or significant publication bias. Higher LDL-C, TC, and TG levels were detected in postmenopausal women than in premenopausal controls.
Conclusion: Unlike increased LDL-C, TC, and TG levels, HDL-C levels in pre- and postmenopausal women were not different in this first meta-analysis of lipid profiles in premenopausal and postmenopausal women. Prospective studies with large populations examining HDL-C levels and functions in women with different menopausal statuses are essential in the future.
Trial registration number: None.
Keywords: Cross-sectional; High-density lipoprotein-cholesterol; Low-density lipoprotein-cholesterol; Postmenopausal; Premenopausal; Total cholesterol; Triglycerides.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Matthan NR, Jalbert SM, Lamon-Fava S, Dolnikowski GG, Welty FK, Barrett HR, Schaefer EJ, Lichtenstein AH. TRL, IDL, and LDL apolipoprotein B-100 and HDL apolipoprotein A-I kinetics as a function of age and menopausal status. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2005;25(8):1691–1696. doi: 10.1161/01.ATV.0000172629.12846.b8. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

