A phase II study of anlotinib in 45 patients with relapsed small cell lung cancer
- PMID: 32557583
- PMCID: PMC7689882
- DOI: 10.1002/ijc.33161
A phase II study of anlotinib in 45 patients with relapsed small cell lung cancer
Abstract
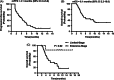
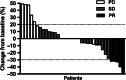
The purpose of this prospective phase II clinical trial was to investigate the efficacy and safety of anlotinib in patients with relapsed small cell lung cancer (SCLC). Forty-five patients with relapsed SCLC were enrolled and treated with anlotinib (one cycle of 12 mg daily for 14 days, discontinued for 7 days, and repeated every 21 days) until disease progression or intolerance of treatment. The primary end point was progression-free survival (PFS). Secondary end points were overall survival (OS), disease control rate (DCR), objective control rate (ORR) and toxicity. The median PFS was 4.1 months (95% confidence interval [CI] 2.4-5.8) and the median OS was 6.1 months (95% CI 2.2-10.0). The OS for the limited-stage subgroup was significantly longer than that of the extensive-stage subgroup (P = .02). The DCR was 67%, and the ORR was 11%. The most common adverse event was hypertension (13%), which was controlled well with antihypertensive drugs. In conclusion, anlotinib has likely efficacy in patients with relapsed SCLC, and the side effects can be well tolerated. A longer OS was observed in limited-stage SCLC patients treated with anlotinib.
Keywords: anlotinib; phase II; small cell lung cancer.
© 2020 The Authors. International Journal of Cancer published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of UICC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Dikshit R, et al. Cancer incidence and mortality worldwide: sources, methods and major patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int J Cancer. 2015;136:E359‐E386. - PubMed
-
- Chen W, Zheng R, Baade PD, et al. Cancer statistics in China, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 2016;66:115‐132. - PubMed
-
- Petrović M, Bukumirić Z, Zdravković V, Mitrović S, Atkinson HD, Jurišić V. The prognostic significance of the circulating neuroendocrine markers chromogranin a, pro‐gastrin‐releasing peptide, and neuron‐specific enolase in patients with small‐cell lung cancer. Med Oncol. 2014;31:823. - PubMed
-
- Howlader N, Noone AM, Krapcho M, et al., eds. SEER Cancer Statistics Review, 1975–2016. Bethesda, MD: National Cancer Institute; 2019. https://seer.cancer.gov/csr/1975_2016/, based on November 2018 SEER data submission, posted to the SEER web site, April 2019.
-
- Jett JR, Schild SE, Kesler KA, Kalemkerian GP. Treatment of small cell lung cancer: diagnosis and management of lung cancer, 3rd ed: American College of Chest Physicians evidence‐based clinical practice guidelines. Chest. 2013;143:e400S‐e419S. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

