A Randomized, Controlled Trial of Exercise for Parkinsonian Individuals With Freezing of Gait
- PMID: 32557868
- PMCID: PMC7722148
- DOI: 10.1002/mds.28128
A Randomized, Controlled Trial of Exercise for Parkinsonian Individuals With Freezing of Gait
Abstract
Background: Exercises with motor complexity induce neuroplasticity in individuals with Parkinson's disease (PD), but its effects on freezing of gait are unknown. The objective of this study was to verify if adapted resistance training with instability - exercises with motor complexity will be more effective than traditional motor rehabilitation - exercises without motor complexity in improving freezing-of-gait severity, outcomes linked to freezing of gait, and brain function.
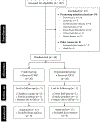
Methods: Freezers were randomized either to the adapted resistance training with instability group (n = 17) or to the active control group (traditional motor rehabilitation, n = 15). Both training groups performed exercises 3 times a week for 12 weeks. The primary outcome was the New Freezing of Gait Questionnaire. Secondary outcomes were freezing of gait ratio (turning task), cognitive inhibition (Stroop-III test), motor signs (Unified Parkinson's Disease Rating Scale part-III [UPDRS-III]), quality of life (PD Questionnaire 39), anticipatory postural adjustment (leg-lifting task) and brain activation during a functional magnetic resonance imaging protocol of simulated anticipatory postural adjustment task. Outcomes were evaluated before and after interventions.
Results: Only adapted resistance training with instability improved all the outcomes (P < 0.05). Adapted resistance training with instability was more effective than traditional motor rehabilitation (in improving freezing-of-gait ratio, motor signs, quality of life, anticipatory postural adjustment amplitude, and brain activation; P < 0.05). Our results are clinically relevant because improvement in the New Freezing of Gait Questionnaire (-4.4 points) and UPDRS-III (-7.4 points) scores exceeded the minimally detectable change (traditional motor rehabilitation group data) and the moderate clinically important difference suggested for PD, respectively. The changes in mesencephalic locomotor region activation and in anticipatory postural adjustment amplitude explained the changes in New Freezing of Gait Questionnaire scores and in freezing-of-gait ratio following adapted resistance training with instability, respectively.
Conclusions: Adapted resistance training with instability is able to cause significant clinical improvement and brain plasticity in freezers. © 2020 International Parkinson and Movement Disorder Society.
Keywords: BOLD; anticipatory postural adjustments; cognitive inhibition; freezers; motor complexity exercises.
© 2020 International Parkinson and Movement Disorder Society.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
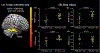
Comment in
-
Letter to the Editor on "A Randomized, Controlled Trial of Exercise for Parkinsonian Individuals With Freezing of Gait".Mov Disord. 2020 Nov;35(11):2122-2123. doi: 10.1002/mds.28294. Mov Disord. 2020. PMID: 33463747 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Reply to: 'Letter to the Editor on "A Randomized Controlled Trial of Exercise for Parkinsonian Individuals With Freezing of Gait"'.Mov Disord. 2020 Nov;35(11):2123-2124. doi: 10.1002/mds.28292. Mov Disord. 2020. PMID: 33463752 No abstract available.
References
-
- Bloem BR, Hausdorff JM, Visser JE, Giladi N. Falls and freezing of gait in Parkinson’s disease: a review of two interconnected, episodic phenomena. Movement disorders : official journal of the Movement Disorder Society 2004;19(8):871–884. - PubMed
-
- Giladi N, Treves TA, Simon ES, et al. Freezing of gait in patients with advanced Parkinson’s disease. J Neural Transm (Vienna) 2001;108(1):53–61. - PubMed
-
- Moore O, Peretz C, Giladi N. Freezing of gait affects quality of life of peoples with Parkinson’s disease beyond its relationships with mobility and gait. Movement disorders : official journal of the Movement Disorder Society 2007;22(15):2192–2195. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

