Mapping Structural Connectivity Using Diffusion MRI: Challenges and Opportunities
- PMID: 32557893
- PMCID: PMC7615246
- DOI: 10.1002/jmri.27188
Mapping Structural Connectivity Using Diffusion MRI: Challenges and Opportunities
Abstract
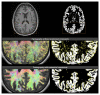
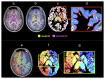
Diffusion MRI-based tractography is the most commonly-used technique when inferring the structural brain connectome, i.e., the comprehensive map of the connections in the brain. The utility of graph theory-a powerful mathematical approach for modeling complex network systems-for analyzing tractography-based connectomes brings important opportunities to interrogate connectome data, providing novel insights into the connectivity patterns and topological characteristics of brain structural networks. When applying this framework, however, there are challenges, particularly regarding methodological and biological plausibility. This article describes the challenges surrounding quantitative tractography and potential solutions. In addition, challenges related to the calculation of global network metrics based on graph theory are discussed.Evidence Level: 5Technical Efficacy: Stage 1.
Keywords: connectomics; diffusion MRI; graph theoretical analysis; network metrics; structural connectome; tractography.
© 2020 The Authors. Journal of Magnetic Resonance Imaging published by Wiley Periodicals LLC. on behalf of International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine.
Figures





References
-
- Bullmore E, Sporns O. Complex brain networks: Graph theoretical analysis of structural and functional systems. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2009;10:186–198. - PubMed
-
- Sporns O. The human connectome: A complex network. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2011;1224:109–125. - PubMed
-
- Bassett DS, Bullmore E. Small-world brain networks. Neuroscientist. 2006;12:512–523. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

