Recent survival trends in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma--Have we made any progress beyond rituximab?
- PMID: 32558356
- PMCID: PMC7402846
- DOI: 10.1002/cam4.3237
Recent survival trends in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma--Have we made any progress beyond rituximab?
Abstract
Background: Population-based studies previously showed an improvement in overall survival (OS) for patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) who received chemoimmunotherapy with rituximab. However, there is limited data (especially at the population level) that show a similar trend in OS improvement, in the most recent time period. We hypothesized that survival for DLBCL patients diagnosed in the United States has continued to improve in recent years and intended to measure outcome improvements.
Methods: Using the SEER-18 registries, we compared the incidence and relative survival rates (RSRs) of DLBCL patients between 2002-2007 and 2008-2013 (availability of novel agents, broader use of autologous hematopoietic cell transplantation and improvement in supportive care). Multivariable Cox regression models were used to assess associations between the year of diagnosis and OS while controlling for age, gender, stage, and ethnicity.
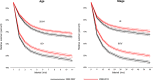
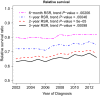
Results: There were a total of 53 439 patients with DLBCL who were diagnosed between 2002 and 2013. Of these, 25 810 were diagnosed during time period-1 and 27 629 diagnosed during time period-2. There was a slight decline in incidence of DLBCL (time period-1 vs time period-2), 7.75 (95% CI = 7.66-7.84) vs 7.43 (95% CI = 7.34-7.52) cases per 100 000 persons, respectively (P < .0001). Overall, there was a modest improvement in DLBCL RSRs, with 5-year RSR improving from 61% (time period-1) to 64% (time period-2) and the improvement was noted across all subsets of patients. On multivariable analysis, patients diagnosed in time period-2 had lower mortality relative to time period-1 (HR = 0.87, 95% CI = 0.85-0.89).
Conclusions: Our study shows an improvement in the outcomes of DLBCL patients beyond the introduction of rituximab, although the magnitude of improvement is small. It will be interesting to see the impact of chimeric antigen receptor-T cell therapy translating to population-level survival in the next 5 years.
Keywords: diffuse large B-cell lymphoma; incidence; population outcomes; relative survival rate; survival.
© 2020 The Authors. Cancer Medicine published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors do not have any relevant conflict of interest pertaining to the manuscript.
Figures
References
-
- Hakulinen T, Seppa K, Lambert PC. Choosing the relative survival method for cancer survival estimation. Eur J Cancer. 2011;47(14):2202‐2210. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources