Solubility-Weighted Index: fast and accurate prediction of protein solubility
- PMID: 32559287
- PMCID: PMC7750957
- DOI: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btaa578
Solubility-Weighted Index: fast and accurate prediction of protein solubility
Abstract
Motivation: Recombinant protein production is a widely used technique in the biotechnology and biomedical industries, yet only a quarter of target proteins are soluble and can therefore be purified.
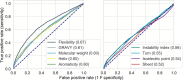
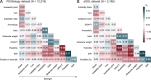
Results: We have discovered that global structural flexibility, which can be modeled by normalized B-factors, accurately predicts the solubility of 12 216 recombinant proteins expressed in Escherichia coli. We have optimized these B-factors, and derived a new set of values for solubility scoring that further improves prediction accuracy. We call this new predictor the 'Solubility-Weighted Index' (SWI). Importantly, SWI outperforms many existing protein solubility prediction tools. Furthermore, we have developed 'SoDoPE' (Soluble Domain for Protein Expression), a web interface that allows users to choose a protein region of interest for predicting and maximizing both protein expression and solubility.
Availability and implementation: The SoDoPE web server and source code are freely available at https://tisigner.com/sodope and https://github.com/Gardner-BinfLab/TISIGNER-ReactJS, respectively. The code and data for reproducing our analysis can be found at https://github.com/Gardner-BinfLab/SoDoPE_paper_2020.
Supplementary information: Supplementary data are available at Bioinformatics online.
© The Author(s) 2020. Published by Oxford University Press.
Figures


References
-
- Acton T.B. et al. (2005) Robotic cloning and protein production platform of the northeast structural genomics consortium. Methods Enzymol., 394, 210–243. - PubMed
-
- Bhandari B.K. et al. (2019) Highly accessible translation initiation sites are predictive of successful heterologous protein expression. BioRxiv, 726752.
-
- Bhaskaran R., Ponnuswamy P.K. (1998) Positional flexibilities of amino acid residues in globular proteins. Int. J. Pept. Protein Res., 32, 241–255. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

