Real-world outcomes of advanced melanoma patients not represented in phase III trials
- PMID: 32559817
- PMCID: PMC7689762
- DOI: 10.1002/ijc.33162
Real-world outcomes of advanced melanoma patients not represented in phase III trials
Abstract
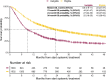
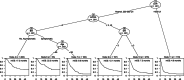
The aim was to provide evidence on systemically treated patients with advanced melanoma not represented in phase III trials to support clinical decision-making. Analysis were performed on advanced melanoma patients diagnosed between 2014 and 2017 in the Netherlands, treated with immune- or targeted therapy, who met ≥1 trial exclusion criteria. These criteria were derived from the KEYNOTE-006 and CHECKMATE-067/-066 phase III trials. Prognostic importance of factors associated with overall survival (OS) was assessed with the Kaplan-Meier method, Cox models, predicted OS probabilities of prognostic subgroups and a conditional inference survival tree (CIST). A nationwide population-based registry was used as data source. Of 2536 systemically treated patients with advanced melanoma, 1004 (40%) patients were ineligible for phase IIII trials. Ineligible patients had a poorer median OS (mOS) compared to eligible patients (8.8 vs 23 months). Eligibility criteria strongly associated with OS in systemically treated ineligible patients were Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group Performance Score (ECOG PS) ≥2, brain metastases (BM) and lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) of >500 U/L. Patients with ECOG PS of ≥2 with or without symptomatic BM had a predicted mOS of 6.5 and 11.3 months and a 3-year survival probability of 9.3% and 23.6%, respectively. The CIST showed the strongest prognostic covariate for survival was LDH, followed by ECOG PS. The prognosis of patients with LDH of >500 U/L is poor, but long-term survival is possible. The prognosis of ineligible patients with advanced melanoma in real-world was very heterogeneous and highly dependent on LDH value, ECOG PS and symptomatic BM.
Keywords: advanced melanoma; decision tree; ineligibility; real-world outcomes; survival.
© 2020 The Authors. International Journal of Cancer published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of UICC.
Conflict of interest statement
A. J. M. v. d. E. has advisory relationships with Amgen, Bristol‐Myers Squibb, Roche, Novartis, MSD, Pierre Fabre, Sanofi, Pfizer, Ipsen, Merck and has received research study grants not related to this article from Sanofi, Roche, Bristol‐Myers Squibb, Idera and TEVA, travel expenses from MSD Oncology, Roche, Pfizer and Sanofi and received speaker honoraria from BMS and Novartis. M. J. B. S. has consultancy relationships with Pierre Fabre, MSD and Novartis. J. W. B. d. G. has advisory relationships with Bristol‐Myers Squibb, Pierre Fabre, Servier, MSD, and Novartis. G. A. P. H. has consultancy/advisory relationships with Amgen, Bristol‐Myers Squibb, Roche, MSD, Pfizer, Novartis, Pierre Fabre and has received research grants not related to this article from Bristol‐Myers Squibb, Seerave. E. K. has consultancy/advisory relationships with Bristol‐Myers Squibb, Novartis, Merck, Pierre Fabre and received research grants not related to this article from Bristol‐Myers Squibb. K. P. M. S. has consultancy/advisory relationships with Bristol‐Myers Squibb, Novartis, MSD, Pierre Fabre and received honoraria from Novartis, MSD and Roche. A. A. M. v. d. V. has consultancy/advisory relationships with Bristol‐Myers Squibb, MSD, Roche, Novartis, Pierre Fabre, Pfizer, Sanofi, Ipsen, Eisai, Merck. J. B. A. G. H. has advisory relationships with Aimm, Achilles Therapeutics, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Bristol‐Myers Squibb, Celsius Therapeutics, GSK, Immunocore, Ipsen, MSD, Merck Serono, Novartis, Neogene Thereapeutics, Neon Therapeutics, Pfizer, Roche/Genentech, Sanofi, Seattle Genetics, Third Rock Ventures, Vaximm and has received research grants not related to this article from Bristol‐Myers Squibb, MSD, Neon Therapeutics and Novartis. All grants were paid to the institutions. The funders had no role in the writing of this article or decision to submit it for publication. All remaining authors have declared no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Ugurel S, Röhmel J, Ascierto PA, et al. Survival of patients with advanced metastatic melanoma: the impact of novel therapies–update 2017. Eur J Cancer. 2017;83:247‐257. - PubMed
-
- Donia M, Kimper‐Karl ML, Høyer KL, Bastholt L, Schmidt H, Svane IM. The majority of patients with metastatic melanoma are not represented in pivotal phase III immunotherapy trials. Eur J Cancer. 2017;74:89‐95. - PubMed
-
- Donia M, Ellebaek E, Øllegaard TH, et al. The real‐world impact of modern treatments on the survival of patients with metastatic melanoma. Eur J Cancer. 2019;108:25‐32. - PubMed
-
- Schadendorf D, Wolchok JD, Stephen Hodi F, et al. Efficacy and safety outcomes in patients with advanced melanoma who discontinued treatment with nivolumab and ipilimumab because of adverse events: a pooled analysis of randomized phase II and III trials. J Clin Oncol. 2017;35:3807‐3814. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

