Performance Assessment of SARS-CoV-2 PCR Assays Developed by WHO Referral Laboratories
- PMID: 32560044
- PMCID: PMC7355678
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm9061871
Performance Assessment of SARS-CoV-2 PCR Assays Developed by WHO Referral Laboratories
Abstract
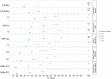
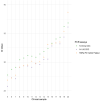
A reliable diagnostic assay is crucial to early detect new COVID-19 cases and limit severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) transmission. Since the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic, the World Health Organization has published several diagnostic molecular approaches developed by referral laboratories, including Charité (Germany), HKU (Hong Kong), China CDC (China), US CDC (United States), and Institut Pasteur, Paris (France). We aimed to compare the sensitivity and specificity of these different RT-PCR assays using SARS-CoV-2 cell culture supernatants and clinical respiratory samples. Overall, the different RT-PCR assays performed well for SARS-CoV-2 detection and were all specific except the N Charité (Germany), and N2 US CDC (United States) assays. RdRp Institut Pasteur (IP2, IP4), N China CDC, and N1 US CDC were found to be the most sensitive assays. The data presented herein are of prime importance to facilitate the equipment choice of diagnostic laboratories, as well as for the development of marketed tests.
Keywords: COVID-19; RT-PCR; SARS-CoV-2; diagnostics; sensitivity.
Conflict of interest statement
S.E., V.E., M.B., G.D., G.B., L.J., E.F., F.M., and A.G. declare no conflict of interest. A.B has received a research grant from bioMérieux. K.B.-P., V.C., L.G., and G.O. are employees at bioMérieux. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization WHO Announces COVID-19 Outbreak a Pandemic. [(accessed on 6 April 2020)]; Available online: http://www.euro.who.int/en/health-topics/health-emergencies/coronavirus-....
-
- World Health Organization Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19)—Situation Report—127. [(accessed on 26 May 2020)]; Available online: https://www.who.int/docs/default-source/coronaviruse/situation-reports/2....
-
- Holmes E.C. Novel 2019 Coronavirus Genome. [(accessed on 24 March 2020)]; Available online: http://virological.org/t/novel-2019-coronavirus-genome/319.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

