Soft Materials for Wearable/Flexible Electrochemical Energy Conversion, Storage, and Biosensor Devices
- PMID: 32560176
- PMCID: PMC7345738
- DOI: 10.3390/ma13122733
Soft Materials for Wearable/Flexible Electrochemical Energy Conversion, Storage, and Biosensor Devices
Abstract
Next-generation wearable technology needs portable flexible energy storage, conversion, and biosensor devices that can be worn on soft and curved surfaces. The conformal integration of these devices requires the use of soft, flexible, light materials, and substrates with similar mechanical properties as well as high performances. In this review, we have collected and discussed the remarkable research contributions of recent years, focusing the attention on the development and arrangement of soft and flexible materials (electrodes, electrolytes, substrates) that allowed traditional power sources and sensors to become viable and compatible with wearable electronics, preserving or improving their conventional performances.
Keywords: embedded mediators; enzymatic biofuel cells; flexible lithium batteries.; flexible polymer electrolyte fuel cells; microbial fuel cells; soft materials; wearable devices.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
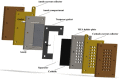








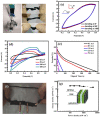
References
-
- Nathan A., Ahnood A., Cole M.T., Lee S., Suzuki Y., Hiralal P., Bonaccorso F., Hasan T., Garcia-Gancedo L., Dyadyusha A. Flexible electronics: The next ubiquitous platform. Proc. IEEE. 2012;100:1486–1517. doi: 10.1109/JPROC.2012.2190168. - DOI
-
- Sun Y., Rogers J.A. Inorganic semiconductors for flexible electronics. Adv. Mater. 2007;19:1897–1916. doi: 10.1002/adma.200602223. - DOI
-
- Shi Q., He T., Lee C. More than energy harvesting–Combining triboelectric nanogenerator and flexible electronics technology for enabling novel micro-/nano-systems. Nano Energy. 2019;57:851–871. doi: 10.1016/j.nanoen.2019.01.002. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

