Role of Changes in State of Bound Water and Tissue Stiffness in Development of Age-Related Diseases
- PMID: 32560459
- PMCID: PMC7361708
- DOI: 10.3390/polym12061362
Role of Changes in State of Bound Water and Tissue Stiffness in Development of Age-Related Diseases
Abstract
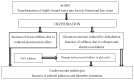
An essential effect of environmental stiffness on biological processes in cells at present is generally accepted. An increase in arterial stiffness with advanced age has been reported in many publications. The aim of the present review is to summarize current information about possible chemical reactions and physical processes that lead to tissue stiffening and result in age-related diseases in order to find methods that can prevent or retard time-dependent tissue stiffening. The analysis of published data shows that bound water acts as a plasticizer of biological tissues, a decrease in bound water content results in an increase in biological tissue stiffness, and increased tissue stiffness leads to NF-kB activation and triggered actin polymerization-NF-kB activation is associated with age-related diseases. It can be suggested that changes in bound water content through changing tissue stiffness can affect cellular processes and the development of pathologies related to aging. Both age-related diseases and COVID-19 may be associated with tight-junction disruption and increased tissue stiffness and permeability.
Keywords: age-related diseases; bound water; hydration; stiffness.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Otsuka Y., Shirakashi R., Hirakawa K. Bound states of water in gelatin discriminated by near-infrared spectroscopy. Japan. J. Appl. Phys. 2017;56:111602. doi: 10.7567/JJAP.56.111602. - DOI
-
- Wolfe J., Bryant G., Koster K. What is “unfreezable water”, how unfreezable is it and how much is there? Cryoletters. 2002;23:157–166. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

