DIY-NAMIC Behavior: A High-Throughput Method to Measure Complex Phenotypes in the Homecage
- PMID: 32561574
- PMCID: PMC7358334
- DOI: 10.1523/ENEURO.0160-20.2020
DIY-NAMIC Behavior: A High-Throughput Method to Measure Complex Phenotypes in the Homecage
Abstract
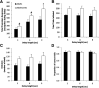
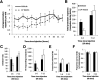
Complex behavioral assessment is necessary to comprehensively assess in vivo manipulations in rodent models for neuropsychiatric disorders. Operant behavioral paradigms provide rich datasets and allow for the careful analysis of behavioral phenotypes. However, one major limitation in these studies is the expense and work-load that are required using traditional methods. The equipment for commercial operant boxes can be prohibitively expensive, and the daily experimenter effort and mouse costs required for these studies is extensive. Rodents are generally trained on task-specific paradigms for months, tested every day for 5-7 d/week. Additionally, appetitive paradigms usually require food restriction and are also commonly run in the non-active light phase of the rodent circadian rhythm. These limitations make operant behavioral testing especially difficult during adolescence, a time period of interest with regards to the development of adult-like phenotypes and a high-risk period for the development of neuropsychiatric disorders, including those which involve impulsive behavior. In order to address these issues, we developed an automated, inexpensive, open-source method which allows the implementation of most standard operant paradigms in the homecage of rodents in shorter time frames without food restriction, and with much less experimenter effort. All construction and code for the do-it-yourself Nautiyal Automated Modular Instrumental Conditioning (DIY-NAMIC) system are open source. We demonstrate their utility here by measuring impulsive behavior in a pharmacology experiment, as well as in adolescent mice.
Keywords: adolescence; automated behavioral testing; behavioral pharmacology; impulsivity; operant; serotonin.
Copyright © 2020 Lee et al.
Figures



References
-
- Balachandran RC, Hatcher KM, Sieg ML, Sullivan EK, Molina LM, Mahoney MM, Eubig PA (2020) Pharmacological challenges examining the underlying mechanism of altered response inhibition and attention due to circadian disruption in adult Long-Evans rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 193:172915. 10.1016/j.pbb.2020.172915 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
