Varied clinical presentation and outcome of SARS-CoV-2 infection in liver transplant recipients: Initial experience at a single center in Madrid, Spain
- PMID: 32562561
- PMCID: PMC7323090
- DOI: 10.1111/tid.13372
Varied clinical presentation and outcome of SARS-CoV-2 infection in liver transplant recipients: Initial experience at a single center in Madrid, Spain
Abstract
Background: Which are the consequences of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection in liver transplant (LT) recipients?
Methods: We attempted to address this question by reviewing our single-center experience during the first 2 months of the pandemics at a high incidence area.
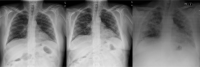
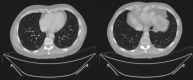
Results: Nineteen adult patients (5 females) were diagnosed by May 5, 2020. Median age was 58 (range 55-72), and median follow-up since transplantation was 83 (range 20-183) months. Cough (84.2%), fever (57.9%), and dyspnea (47.4%) were the most common symptoms. Thirteen patients (68.4%) had pneumonia in x-ray/CT scan. Hydroxychloroquine was administered in 11 patients, associated with lopinavir/ritonavir and interferon β in 2 cases each. Immunomodulatory therapy with tocilizumab was used in 2 patients. Immunosuppression (IS) was halted in one patient and modified in only other two due to potential drug interactions. Five (26.3%) patients were managed as outpatient. Two patients (10.5%) died, 10 (52.6%) were discharged home, and 2 (10.5%) were still hospitalized after a median follow-up of 41 days from the onset of symptoms. Baseline IS regimen remained unchanged in all surviving recipients, with good liver function.
Conclusions: Our preliminary experience shows a broad spectrum of disease severity in LT patients with COVID-19, with a favorable outcome in most of them without needing to modify baseline IS.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-CoV2; immunosuppression; liver transplant; prognosis.
© 2020 Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Figures
Similar articles
-
SARS-CoV-2 infection in kidney transplant recipients: Experience of the italian marche region.Transpl Infect Dis. 2020 Oct;22(5):e13377. doi: 10.1111/tid.13377. Epub 2020 Jul 28. Transpl Infect Dis. 2020. PMID: 32573895 Free PMC article.
-
COVID-19 in kidney transplant recipients: A multicenter experience in Istanbul.Transpl Infect Dis. 2020 Oct;22(5):e13371. doi: 10.1111/tid.13371. Epub 2020 Jul 13. Transpl Infect Dis. 2020. PMID: 32657540 Free PMC article.
-
Outcome of COVID-19 in liver transplant recipients: A preliminary report from Northwestern Italy.Transpl Infect Dis. 2020 Oct;22(5):e13353. doi: 10.1111/tid.13353. Epub 2020 Jun 16. Transpl Infect Dis. 2020. PMID: 32500942 Free PMC article.
-
COVID-19 pneumonia in kidney transplant recipients-Where we are?Transpl Infect Dis. 2020 Oct;22(5):e13306. doi: 10.1111/tid.13306. Epub 2020 May 26. Transpl Infect Dis. 2020. PMID: 32364677 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Coronavirus disease 2019 in an orthotopic liver transplant recipient living with human immunodeficiency virus.Transpl Infect Dis. 2020 Oct;22(5):e13351. doi: 10.1111/tid.13351. Epub 2020 Jun 17. Transpl Infect Dis. 2020. PMID: 32500666 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
T cell-mediated response to SARS-CoV-2 in liver transplant recipients with prior COVID-19.Am J Transplant. 2021 Aug;21(8):2785-2794. doi: 10.1111/ajt.16708. Epub 2021 Jun 25. Am J Transplant. 2021. PMID: 34092033 Free PMC article.
-
Correlation between COVID-19 and hepatitis B: A systematic review.World J Gastroenterol. 2022 Dec 14;28(46):6599-6618. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i46.6599. World J Gastroenterol. 2022. PMID: 36569273 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnosis, treatment protocols, and outcomes of liver transplant recipients infected with COVID-19.World J Clin Cases. 2023 Apr 6;11(10):2140-2159. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v11.i10.2140. World J Clin Cases. 2023. PMID: 37122505 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinical Manifestations and Characterization of COVID-19 in Liver Transplant Recipients: A Systematic Review of Case Reports and Case Series.Ethiop J Health Sci. 2021 Mar;31(2):429-438. doi: 10.4314/ejhs.v31i2.26. Ethiop J Health Sci. 2021. PMID: 34158795 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of immunosuppression maintenance in solid organ transplant recipients with COVID-19: Systematic review and meta-analysis.Transpl Infect Dis. 2021 Aug;23(4):e13595. doi: 10.1111/tid.13595. Epub 2021 Mar 18. Transpl Infect Dis. 2021. PMID: 33641202 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

