Insulin restores the neurochemical effects of nicotine in the mesolimbic pathway of diabetic rats
- PMID: 32562571
- PMCID: PMC7749845
- DOI: 10.1111/jnc.15104
Insulin restores the neurochemical effects of nicotine in the mesolimbic pathway of diabetic rats
Abstract
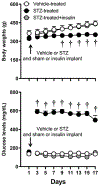
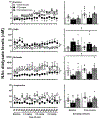
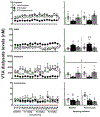
This study examined whether insulin modulates the neurochemical effects of nicotine in the mesolimbic pathway of diabetic rats. The rats received vehicle or streptozotocin (STZ) to induce hypoinsulinemia. A subset of STZ-treated rats was implanted with insulin pellets that rapidly normalized glucose levels. Two-weeks later, dialysis probes were implanted into the nucleus accumbens (NAc) and ipsilateral ventral tegmental area (VTA). The next day, dialysate samples were collected during baseline and then following systemic administration of nicotine. Samples were also collected following intra-VTA administration of the gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA)A receptor antagonist, bicuculline. Dopamine, GABA, glutamate, and acetylcholine (ACh) levels were assessed using liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry (LC/MS). The results revealed that vehicle-treated rats displayed a nicotine-induced increase in NAc dopamine levels. In contrast, STZ-treated rats did not display any changes in NAc dopamine following nicotine administration, an effect that was likely related to a concomitant increase in GABA and decrease in glutamate levels in both the NAc and VTA. Intra-VTA administration of bicuculline increased NAc dopamine in vehicle-treated rats, and this effect was absent in STZ-treated rats. Vehicle-treated rats displayed a nicotine-induced increase in ACh levels in the NAc (but not VTA), an effect that was lower in the NAc of STZ-treated rats. Insulin supplementation normalized the neurochemical effects of nicotine in the NAc and VTA of STZ-treated rats, suggesting that insulin modulates the neurochemical effects of nicotine in the mesolimbic pathway of diabetic rats.
Keywords: amino acids; diabetes; dopamine; insulin; micro-dialysis; tobacco use.
© 2020 International Society for Neurochemistry.
Figures



References
-
- Arison RN, Ciaccio EI, Glitzer MS, Cassaro JA, and Pruss MP (1967) Light and electron microscopy of lesions in rats rendered diabetic with streptozotocin. Diabetes. 16, 51–56. - PubMed
-
- Bishop FK, Maahs DM, Snell-Bergeon JK, Ogden LG, Kinney GL, and Rewers M (2009) Lifestyle risk factors for atherosclerosis in adults with type 1 diabetes. Diab Vasc Dis Res. 64, 269–275. - PubMed
-
- Bitar M, Koulu M, Rapoport SI and Linnoila M (1986) Diabetes-induced alteration in brain monoamine metabolism in rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 236, 432–437. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

