A Grading System for Invasive Pulmonary Adenocarcinoma: A Proposal From the International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer Pathology Committee
- PMID: 32562873
- PMCID: PMC8362286
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jtho.2020.06.001
A Grading System for Invasive Pulmonary Adenocarcinoma: A Proposal From the International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer Pathology Committee
Abstract
Introduction: A grading system for pulmonary adenocarcinoma has not been established. The International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer pathology panel evaluated a set of histologic criteria associated with prognosis aimed at establishing a grading system for invasive pulmonary adenocarcinoma.
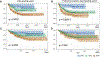
Methods: A multi-institutional study involving multiple cohorts of invasive pulmonary adenocarcinomas was conducted. A cohort of 284 stage I pulmonary adenocarcinomas was used as a training set to identify histologic features associated with patient outcomes (recurrence-free survival [RFS] and overall survival [OS]). Receiver operating characteristic curve analysis was used to select the best model, which was validated (n = 212) and tested (n = 300, including stage I-III) in independent cohorts. Reproducibility of the model was assessed using kappa statistics.
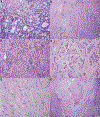
Results: The best model (area under the receiver operating characteristic curve [AUC] = 0.749 for RFS and 0.787 for OS) was composed of a combination of predominant plus high-grade histologic pattern with a cutoff of 20% for the latter. The model consists of the following: grade 1, lepidic predominant tumor; grade 2, acinar or papillary predominant tumor, both with no or less than 20% of high-grade patterns; and grade 3, any tumor with 20% or more of high-grade patterns (solid, micropapillary, or complex gland). Similar results were seen in the validation (AUC = 0.732 for RFS and 0.787 for OS) and test cohorts (AUC = 0.690 for RFS and 0.743 for OS), confirming the predictive value of the model. Interobserver reproducibility revealed good agreement (k = 0.617).
Conclusions: A grading system based on the predominant and high-grade patterns is practical and prognostic for invasive pulmonary adenocarcinoma.
Keywords: Adenocarcinoma; Lung; Model; Prognosis; Tumor grading.
Copyright © 2020 International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Amin MB, Edge S, Greene F, et al. , eds. AJCC Cancer Staging Manual. 8th ed.Chicago, IL: Springer International Publishing; 2017.
-
- Rabe K, Snir OL, Bossuyt V, Harigopal M, Celli R, Reisenbichler ES. Interobserver variability in breast carcinoma grading results in prognostic stage differences. Hum Pathol 2019;94:51–57. - PubMed
-
- Helpap B, Ringli D, Tonhauser J, et al. The significance of accurate determination of Gleason score for therapeutic options and prognosis of prostate cancer. Pathol Oncol Res 2016;22:349–356. - PubMed
-
- Rice-Stitt T, Valencia-Guerrero A, Cornejo KM, Wu CL. Updates in histologic grading of urologic neoplasms. Arch Pathol Lab Med 2020;144:335–343. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

