Do I feel or do I know? Neuroimaging meta-analyses on the multiple facets of empathy
- PMID: 32562973
- PMCID: PMC7390692
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cortex.2020.04.031
Do I feel or do I know? Neuroimaging meta-analyses on the multiple facets of empathy
Abstract
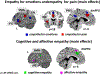
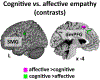
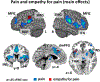
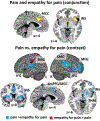
Empathy is a multidimensional construct including affective and cognitive components while maintaining the distinction between one-self and others. Our meta-analyses focused on shared and distinct networks underlying cognitive (taking somebody else's perspective in emotional/painful situations) and affective (self-referentially feeling somebody else's emotions/pain) empathy for various states including painful and emotional situations. Furthermore, a comparison with direct pain experience was carried out. For cognitive empathy, consistent activation in the anterior dorsal medial frontal gyrus (dmPFG) and the supramarginal gyrus (SMG) occurred. For affective empathy, convergent activation of the posterior dmPFG and the inferior frontal gyrus (IFG) was found. Consistent activation of the anterior insula (AI), the anterior dmPFG and the SMG was observed for empathy for pain, while convergent recruitment of the temporo-parietal junction, precuneus, posterior dmPFG, and the IFG was revealed in the meta-analysis across empathy for emotion experiments. The AI and the dmPFG/mid-cingulate cortex (MCC) showed overlapping as well as distinct neural activation for pain processing and empathy for pain. Taken together, we were able to show difference in the meta-analytic networks across cognitive and affective empathy as well as for pain and empathy processing. Based on the current results, distinct functions along the midline structures of the brain during empathy processing are apparent. Our data are lending further support for a multidimensional concept of empathy.
Keywords: ACC/MCC/dmPFG; Cognitive and affective empathy; Emotions; Insula; Pain; TPJ.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Financial Disclosure and conflict of interest
The authors report no biomedical financial interests or potential conflicts of interest in relation to the manuscript.
Figures
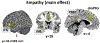
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

