Metabolic Cooperation among Commensal Bacteria Supports Drosophila Juvenile Growth under Nutritional Stress
- PMID: 32563155
- PMCID: PMC7305377
- DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2020.101232
Metabolic Cooperation among Commensal Bacteria Supports Drosophila Juvenile Growth under Nutritional Stress
Abstract
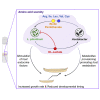
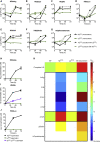
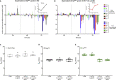
The gut microbiota shapes animal growth trajectory in stressful nutritional environments, but the molecular mechanisms behind such physiological benefits remain poorly understood. The gut microbiota is mostly composed of bacteria, which construct metabolic networks among themselves and with the host. Until now, how the metabolic activities of the microbiota contribute to host juvenile growth remains unknown. Here, using Drosophila as a host model, we report that two of its major bacterial partners, Lactobacillus plantarum and Acetobacter pomorum, engage in a beneficial metabolic dialogue that boosts host juvenile growth despite nutritional stress. We pinpoint that lactate, produced by L. plantarum, is utilized by A. pomorum as an additional carbon source, and A. pomorum provides essential amino acids and vitamins to L. plantarum. Such bacterial cross-feeding provisions a set of anabolic metabolites to the host, which may foster host systemic growth despite poor nutrition.
Keywords: Biological Sciences; Microbiology; Microbiome.
Copyright © 2020 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Interests The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures




References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

