Autoinflammatory and autoimmune conditions at the crossroad of COVID-19
- PMID: 32563547
- PMCID: PMC7296326
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jaut.2020.102506
Autoinflammatory and autoimmune conditions at the crossroad of COVID-19
Abstract
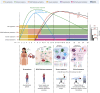
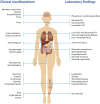
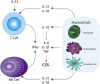
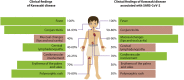
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) has been categorized as evolving in overlapping phases. First, there is a viral phase that may well be asymptomatic or mild in the majority, perhaps 80% of patients. The pathophysiological mechanisms resulting in minimal disease in this initial phase are not well known. In the remaining 20% of cases, the disease may become severe and/or critical. In most patients of this latter group, there is a phase characterized by the hyperresponsiveness of the immune system. A third phase corresponds to a state of hypercoagulability. Finally, in the fourth stage organ injury and failure occur. Appearance of autoinflammatory/autoimmune phenomena in patients with COVID-19 calls attention for the development of new strategies for the management of life-threatening conditions in critically ill patients. Antiphospholipid syndrome, autoimmune cytopenia, Guillain-Barré syndrome and Kawasaki disease have each been reported in patients with COVID-19. Here we present a scoping review of the relevant immunological findings in COVID-19 as well as the current reports about autoinflammatory/autoimmune conditions associated with the disease. These observations have crucial therapeutic implications since immunomodulatory drugs are at present the most likely best candidates for COVID-19 therapy. Clinicians should be aware of these conditions in patients with COVID-19, and these observations should be considered in the current development of vaccines.
Keywords: Antiphospholipid syndrome; Autoimmunity; COVID-19; Cytokine storm syndrome; Cytopenia; Guillain-Barré syndrome; Kawasaki disease; SARS-CoV-2; Vaccines.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- WHO . WHO; 2020. Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19)situation Report – 52.
-
- Zuo Y., Yalavarthi S., Shi H., Gockman K., Zuo M., Madison J.A., Blair C., Weber A., Barnes B.J., Egeblad M., Woods R.J., Kanthi Y., Knight J.S. Neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs) as markers of disease severity in COVID-19. MedRxiv. 2020 doi: 10.1101/2020.04.09.20059626. In press. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

