Amputation in crush syndrome: A case report
- PMID: 32563818
- PMCID: PMC7306514
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijscr.2020.05.087
Amputation in crush syndrome: A case report
Abstract
Introduction: Crush syndrome (CS) is a condition with a high morbidity and mortality due to severe electrolyte disorders, circulatory dysfunction and multiple organ failure, secondary to severe rhabdomyolysis and reperfusion injuries. There is controversy about the role of fasciotomy in the treatment of compartment syndromes due to crush injuries and it is still unknown if early amputation has patient-centered benefits.
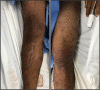
Case presentation: This is a 29-year-old patient whose lower body was trapped for 50 h under a 40-meter landslide. Upon admission the left thigh was edematous and painful. Laboratories revealed a creatinine of 1.58 mg/dL, hyperkalemia, metabolic acidosis, hyperlactatemia and creatinine phosphokinase (CPK) of 88,700 U/L, suggesting CS. Despite fluid and bicarbonate infusion his renal function worsened, CPK rose and left thigh became more tense, so a fasciotomy was performed. He developed a distributive shock refractory to vasopressors, steroids and methylene blue so amputation was proposed. Two hours after amputation the vasopressor support was nearly withdrawn.
Discussion: This case suggests a potential benefit of amputation in patients with CS and progressive deterioration despite aggressive resuscitation. It also invites to think if this is a decision that should be considered before the establishment or in the initial stages of the syndrome, even if the viability of the extremity is still questionable.
Conclusion: The presence of risk factors for poor prognosis can favor amputation despite the apparent viability of the limb and the morbidity of losing an extremity.
Keywords: Amputation; Crush injuries; Crush syndrome; Fasciotomy; Rhabdomyolysis.
Copyright © 2020 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Jagodzinski N.A., Weerasinghe C., Porter K. Crush injuries and crush syndrome – a review. Part 1: the systemic injury. Trauma. 2010;12:69–88.
-
- Oda J., Tanaka H., Yoshioka T., Iwai A., Yamamura H., Ishikawa K. Analysis of 372 patients with Crush syndrome caused by the Hanshin-Awaji earthquake. J. Trauma. 1997;42(3):470–475. discussion 5-6. - PubMed
-
- Sever M.S., Erek E., Vanholder R., Akoglu E., Yavuz M., Ergin H. Clinical findings in the renal victims of a catastrophic disaster: the Marmara earthquake. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2002;17(11):1942–1949. - PubMed
-
- Peek-Asa C., Kraus J.F., Bourque L.B., Vimalachandra D., Yu J., Abrams J. Fatal and hospitalized injuries resulting from the 1994 Northridge earthquake. Int. J. Epidemiol. 1998;27(3):459–465. - PubMed
-
- Agha R.A., Borrelli M.R., Farwana R., Koshy K., Fowler A.J., Orgill D.P. The SCARE 2018 statement: updating consensus surgical CAse REport (SCARE) guidelines. Int. J. Surg. 2018;60:132–136. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources