The Role of Genetic Sex and Mitochondria in Response to COVID-19 Infection
- PMID: 32564017
- PMCID: PMC7360490
- DOI: 10.1159/000508560
The Role of Genetic Sex and Mitochondria in Response to COVID-19 Infection
Abstract
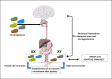
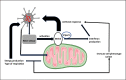
The difference between the female and male immune response to COVID-19 infection, and infections in general, is multifactorial. The well-known determiners of the immune response, such as X and Y chromosomes, sex hormones, and microbiota, are functionally interconnected and influence each other in shaping the organism's immunity. We focus our commentary on the interplay between the genetic sex and mitochondria and how this may affect a sex-dependent immune response in COVID-19 infection. Realizing the existence of these interactions may help in designing novel methods or fine-tuning the existing and routine therapies to fight COVID-19 and other infections.
Keywords: COVID-19; Immunity; Macrophages; Melatonin; SARS-CoV-2; X chromosome; Y chromosome.
© 2020 S. Karger AG, Basel.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors do not have conflict of interest and have nothing to disclose.
Figures

References
-
- Klein SL, Flanagan KL. Sex differences in immune responses. Nat Rev Immunol. 2016;16((10)):626–38. - PubMed
-
- Archive.ensembl.org/Homo_sapiensChromosome X: 1-1 − Chromosome summary − Homo sapiens. http://mar2017.archive.ensembl.org/Homo_sapiens/Location/Chromosome?r=X.
-
- Bianchi I, Lleo A, Gershwin ME, Invernizzi P. The X chromosome and immune associated genes. J Autoimmun. 2012;38((2–3)):J187–92. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

