Superiority of a Novel Mp1p Antigen Detection Enzyme Immunoassay Compared to Standard BACTEC Blood Culture in the Diagnosis of Talaromycosis
- PMID: 32564074
- PMCID: PMC8282318
- DOI: 10.1093/cid/ciaa826
Superiority of a Novel Mp1p Antigen Detection Enzyme Immunoassay Compared to Standard BACTEC Blood Culture in the Diagnosis of Talaromycosis
Abstract
Background: Talaromycosis is an invasive mycosis endemic in Southeast Asia and causes substantial morbidity and mortality in individuals with advanced human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) disease. Current diagnosis relies on isolating Talaromyces marneffei in cultures, which takes up to 14 days and is detectable only during late-stage infection, leading to high mortality.
Methods: In this retrospective case-control study, we assessed the accuracy of a novel Mp1p antigen-detecting enzyme immunoassay (EIA) in stored plasma samples of 372 patients who had culture-proven talaromycosis from blood or sterile body fluids (reference standard) and 517 individuals without talaromycosis (338 healthy volunteers; 179 with other infections). All participants were recruited between 2011 and 2017 in Vietnam.
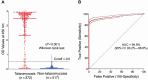
Results: Of cases and controls, 66.1% and 75.4%, respectively, were male; the median age was 33 and 37, respectively. All cases were HIV infected; median CD4 count was 10 cells/μL. At an optical density cutoff of 0.5, the specificity was 98.1% (95% CI, 96.3%-99.0%); the sensitivity was superior to blood culture (86.3% [95% CI, 82.3%-89.5%] vs 72.8% [95% CI, 68.0%-77.2%]) (P < .001, McNemar test). The time to diagnosis was 6 hours vs 6.6 ± 3.0 days for blood culture. Paired plasma and urine testing in the same patients (n = 269) significantly increased sensitivity compared to testing plasma alone or testing urine alone (P < .001 and P = .02, respectively, McNemar test).
Conclusions: The Mp1p EIA is highly specific and is superior in sensitivity and time to diagnosis compared to blood culture for the diagnosis of talaromycosis. Paired plasma and urine testing further increases sensitivity, introducing a new tool for rapid diagnosis, enabling early treatment and potentially reducing mortality.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT04033120.
Keywords: Penicillium marneffei; Talaromyces marneffei; Mp1p enzyme immunoassay; penicilliosis; talaromycosis.
© The Author(s) 2020. Published by Oxford University Press for the Infectious Diseases Society of America.
Figures
References
-
- Limper AH, Adenis A, Le T, Harrison TS. Fungal infections in HIV/AIDS. Lancet Infect Dis 2017; 17:e334–43. - PubMed
-
- Hu Y, Zhang J, Li X, et al. Penicillium marneffei infection: an emerging disease in mainland China. Mycopathologia 2013; 175:57–67. - PubMed
-
- Sirisanthana T, Supparatpinyo K. Epidemiology and management of penicilliosis in human immunodeficiency virus–infected patients. Int J Infect Dis 1998; 3:48–53. - PubMed
-
- Jiang J, Meng S, Huang S, et al. Effects of Talaromyces marneffei infection on mortality of HIV/AIDS patients in southern China: a retrospective cohort study. Clin Microbiol Infect 2019; 25:233–41. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Supplementary concepts
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

