GlycA, a novel marker for low grade inflammation, reflects gut microbiome diversity and is more accurate than high sensitive CRP in reflecting metabolomic profile
- PMID: 32564244
- PMCID: PMC7306047
- DOI: 10.1007/s11306-020-01695-x
GlycA, a novel marker for low grade inflammation, reflects gut microbiome diversity and is more accurate than high sensitive CRP in reflecting metabolomic profile
Abstract
Introduction: Gut microbiota is, along with adipose tissue, recognized as a source for many metabolic and inflammatory disturbances that may contribute to the individual's state of health.
Objectives: We investigated in cross-sectional setting the feasibility of utilizing GlycA, a novel low grade inflammatory marker, and traditional low grade inflammatory marker, high sensitivity CRP (hsCRP), in reflecting serum metabolomics status and gut microbiome diversity.
Methods: Fasting serum samples of overweight/obese pregnant women (n = 335, gestational weeks: mean 13.8) were analysed for hsCRP by immunoassay, GlycA and metabolomics status by NMR metabolomics and faecal samples for gut microbiome diversity by metagenomics. The benefits of GlycA as a metabolic marker were investigated against hsCRP.
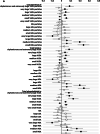
Results: The GlycA concentration correlated with more of the metabolomics markers (144 out of 157), than hsCRP (55 out of 157) (FDR < 0.05). The results remained essentially the same when potential confounding factors known to associate with GlycA and hsCRP levels were taken into account (P < 0.05). This was attributable to the detected correlations between GlycA and the constituents and concentrations of several sized VLDL-particles and branched chain amino acids, which were statistically non-significant with regard to hsCRP. GlycA, but not hsCRP, correlated inversely with gut microbiome diversity.
Conclusion: GlycA is a superior marker than hsCRP in assessing the metabolomic profile and gut microbiome diversity. It is proposed that GlycA may act as a novel marker that reflects both the gut microbiome and adipose tissue originated metabolic aberrations; this proposal will need to be verified with regard to clinical outcomes.
Clinical trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov, NCT01922791, August 14, 2013.
Keywords: GlycA; Gut microbiome diversity; Low grade inflammation; Metabolomics; hsCRP.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declares that he/she has no conflict of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Fizelova M, Jauhiainen R, Kangas AJ, Soininen P, Ala-Korpela M, Kuusisto J, et al. Differential associations of inflammatory markers with insulin sensitivity and secretion: The prospective METSIM study. Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism. 2017;102(9):3600–3609. doi: 10.1210/jc.2017-01057. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
