Technologies and Standardization in Research on Extracellular Vesicles
- PMID: 32564882
- PMCID: PMC7302792
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tibtech.2020.05.012
Technologies and Standardization in Research on Extracellular Vesicles
Abstract
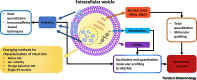
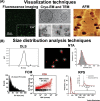
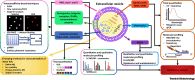
Extracellular vesicles (EVs) are phospholipid bilayer membrane-enclosed structures containing RNAs, proteins, lipids, metabolites, and other molecules, secreted by various cells into physiological fluids. EV-mediated transfer of biomolecules is a critical component of a variety of physiological and pathological processes. Potential applications of EVs in novel diagnostic and therapeutic strategies have brought increasing attention. However, EV research remains highly challenging due to the inherently complex biogenesis of EVs and their vast heterogeneity in size, composition, and origin. There is a need for the establishment of standardized methods that address EV heterogeneity and sources of pre-analytical and analytical variability in EV studies. Here, we review technologies developed for EV isolation and characterization and discuss paths toward standardization in EV research.
Keywords: characterization; exosomes; extracellular vesicles; isolation; molecular profiling; standardization.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Harding C. Endocytosis and intracellular processing of transferrin and colloidal gold-transferrin in rat reticulocytes: demonstration of a pathway for receptor shedding. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 1984;35:256–263. - PubMed
-
- van Niel G. Shedding light on the cell biology of extracellular vesicles. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2018;19:213–228. - PubMed
-
- Cai H. Coats, tethers, Rabs, and SNAREs work together to mediate the intracellular destination of a transport vesicle. Dev. Cell. 2007;12:671–682. - PubMed
-
- Bonifacino J.S., Glick B.S. The mechanisms of vesicle budding and fusion. Cell. 2004;1162:153–166. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

