Carthamus tinctorius L. Extract ameliorates cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats by regulating matrix metalloproteinases and apoptosis
- PMID: 32565598
- PMCID: PMC7282686
- DOI: 10.4103/ijp.IJP_400_18
Carthamus tinctorius L. Extract ameliorates cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats by regulating matrix metalloproteinases and apoptosis
Abstract
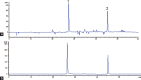
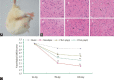
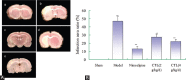
We investigate the protective effect of Carthamus tinctorius L. (CTL, also known as Honghua in China or Safflower) on cerebral ischemia-reperfusion and explored the possible mechanisms on regulating apoptosis and matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs). High-performance liquid chromatography method with diode array detection analysis was established to analyze the components of CTL. Middle cerebral artery occlusion rats model was established to evaluate Neurological Function Score and hematoxylin-eosin staining, as well as triphenyltetrazolium was used to examine the infarction area ratio. Transferase-mediated dUTP nick-end labeling was performed for the apoptosis. Apoptosis-related factors, including B-cell lymphoma-2 (Bcl-2), Bax and Caspase3, and MMPs-related MMP2, MMP9, tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases 1 (TIMP1) in ischemic brain, were assayed by Western blot, reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction, and immunohistochemistry. The data showed that CTL (2, 4 g crude drug/kg/d) treatment could significantly reduce the ischemic damage in brain tissue and improve a significant neurological function score. In addition, CTL could also attenuate apoptosis degree of brain tissues and regulate Bcl-2, Bax, and Caspase 3 and also have a significant decrease on MMP-9 expression, followed by a significant increase of TIMP1 protein expression. These findings indicated that regulation of CTL on apoptosis and MMPs contributed to its protective effect on ischemia/reperfusion injury.
Keywords: Apoptosis; Carthamus tinctorius L.; cerebral ischemia-reperfusion; matrix metalloprotein.
Copyright: © 2020 Indian Journal of Pharmacology.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

