A Comparative Study of the Diagnostic and Prognostic Utility of Soluble Urokinase-type Plasminogen Activator Receptor and Procalcitonin in Patients with Sepsis and Systemic Inflammation Response Syndrome
- PMID: 32565634
- PMCID: PMC7297249
- DOI: 10.5005/jp-journals-10071-23385
A Comparative Study of the Diagnostic and Prognostic Utility of Soluble Urokinase-type Plasminogen Activator Receptor and Procalcitonin in Patients with Sepsis and Systemic Inflammation Response Syndrome
Abstract
Introduction: Differentiation between sepsis and systemic inflammation response syndrome (SIRS) remains a diagnostic challenge for clinicians as both may have similar clinical presentation. A quick and accurate diagnostic tool that can discriminate between these two conditions would aid in appropriate therapeutic decision-making. This prospective study was conducted to evaluate the diagnostic and prognostic utility of soluble urokinase-type plasminogen activator receptor (suPAR) and procalcitonin (PCT) in sepsis and SIRS patients.
Materials and methods: Eighty-eight patients were enrolled, of which 29 were SIRS and 59 were sepsis patients. The levels of suPAR and PCT were measured on the day of admission (day 1), day 3, and day 7.
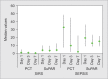
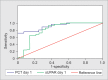
Results: The levels of suPAR and PCT were significantly higher (p = 0.05 and p < 0.001, respectively) in sepsis group as compared to the SIRS group. The soluble urokinase-type plasminogen activator receptor was a better diagnostic tool in predicting sepsis over PCT [area under curve (AUC) 0.89 vs 0.82] on day 1. The best cutoff for suPAR was 5.58 pg/mL [96% sensitivity and 90% negative predictive value (NPV)] and the best cut-off for PCT was 1.96 ng/mL (93.1% sensitivity and 80% NPV). However, PCT had better prognostic trends (p = 0.006) to identify nonsurvivors in sepsis group.
Conclusion: Our findings suggest that both suPAR and PCT can be used as potential test tools to differentiate between SIRS and sepsis. Procalcitonin showed significant prognostic trends to identify nonsurvivors. The soluble urokinase-type plasminogen activator receptor showed better diagnostic potential than PCT on day 1.
Clinical significance: Both suPAR and PCT can be used as surrogate biomarkers to distinguish sepsis from SIRS. Procalcitonin showing a significant prognostic trend to identify nonsurvivors can help the clinicians to take relevant clinical decisions. Also, the use of biomarkers like PCT and suPAR could reduce the inappropriate use of antibiotics in noninfective SIRS.
How to cite this article: Sharma A, Ray S, Mamidipalli R, Kakar A, Chugh P, Jain R, et al. A Comparative Study of the Diagnostic and Prognostic Utility of Soluble Urokinase-type Plasminogen Activator Receptor and Procalcitonin in Patients with Sepsis and Systemic Inflammation Response Syndrome. Indian J Crit Care Med 2020;24(4):245-251.
Keywords: Procalcitonin; Sepsis; Soluble urokinase-type plasminogen activator receptor; Systemic inflammation response syndrome.
Copyright © 2020; Jaypee Brothers Medical Publishers (P) Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Source of support: ViroGates Conflict of interest: None
Figures
References
-
- Hall MJ, Williams SN, DeFrances CJ, Golosinskiy A. Inpatient care for septicemia or sepsis: a challenge for patients and hospitals. NCHS Data Brief. 2011;(62):1–8. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
