Tyrosine triple mutated AAV2-BDNF gene therapy in an inner retinal injury model induced by intravitreal injection of N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA)
- PMID: 32565669
- PMCID: PMC7300199
Tyrosine triple mutated AAV2-BDNF gene therapy in an inner retinal injury model induced by intravitreal injection of N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA)
Abstract
Purpose: Glaucoma is a group of chronic optic neuropathies characterized by the degeneration of retinal ganglion cells (RGCs) and their axons, and they ultimately cause blindness. Because neuroprotection using neurotrophic factors against RGC loss has been proven a beneficial strategy, extensive attempts have been made to perform gene transfer of neurotrophic proteins. This study used the inner retinal injury mouse model to evaluate the neuroprotective effect of tyrosine triple mutated and self-complementary adeno-associated virus (AAV) encoding brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF; tm-scAAV2-BDNF).
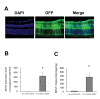
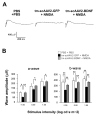
Methods: C57BL/6J mice were intravitreally injected with 1 μl of tm-scAAV2-BDNF and its control AAV at a titer of 6.6 E+13 genome copies/ml. Three weeks later, 1 μl of 2 mM N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) was administered in the same way as the viral injection. Six days after the NMDA injection, we assessed the dark-adapted electroretinography (ERG). Mice were sacrificed at one week after the NMDA injection, followed by RNA quantification, protein detection, and histopathological analysis.
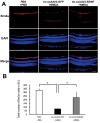
Results: The RNA expression of BDNF in retinas treated with tm-scAAV2-BDNF was about 300-fold higher than that of its control AAV. Meanwhile, the expression of recombinant BDNF protein increased in retinas treated with tm-scAAV2-BDNF. In addition, histological analysis revealed that tm-scAAV2-BDNF prevented thinning of the inner retina. Furthermore, b-wave amplitudes of the tm-scAAV2-BDNF group were significantly higher than those of the control vector group. Histopathological and electrophysiological evaluations showed that tm-scAAV2-BDNF treatment offered significant protection against NMDA toxicity.
Conclusions: Results showed that tm-scAAV2-BDNF-treated retinas were resistant to NMDA injury, while retinas treated with the control AAV exhibited histopathological and functional changes after the administration of NMDA. These results suggest that tm-scAAV2-BDNF is potentially effective against inner retinal injury, including normal tension glaucoma.
Copyright © 2020 Molecular Vision.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Use of Gene Therapy in Retinal Ganglion Cell Neuroprotection: Current Concepts and Future Directions.Biomolecules. 2021 Apr 15;11(4):581. doi: 10.3390/biom11040581. Biomolecules. 2021. PMID: 33920974 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tyrosine triple mutated AAV2-BDNF gene therapy in a rat model of transient IOP elevation.Mol Vis. 2016 Jul 16;22:816-26. eCollection 2016. Mol Vis. 2016. PMID: 27440998 Free PMC article.
-
Neuroprotection of retinal ganglion cells by a novel gene therapy construct that achieves sustained enhancement of brain-derived neurotrophic factor/tropomyosin-related kinase receptor-B signaling.Cell Death Dis. 2018 Sep 26;9(10):1007. doi: 10.1038/s41419-018-1041-8. Cell Death Dis. 2018. PMID: 30258047 Free PMC article.
-
Adeno-associated viruses containing bFGF or BDNF are neuroprotective against excitotoxicity.Curr Eye Res. 2004 Dec;29(6):379-86. doi: 10.1080/02713680490517872. Curr Eye Res. 2004. PMID: 15764082
-
A Comparative Analysis of Models for AAV-Mediated Gene Therapy for Inherited Retinal Diseases.Cells. 2024 Oct 15;13(20):1706. doi: 10.3390/cells13201706. Cells. 2024. PMID: 39451224 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor in Alzheimer's disease and its pharmaceutical potential.Transl Neurodegener. 2022 Jan 28;11(1):4. doi: 10.1186/s40035-022-00279-0. Transl Neurodegener. 2022. PMID: 35090576 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Use of Gene Therapy in Retinal Ganglion Cell Neuroprotection: Current Concepts and Future Directions.Biomolecules. 2021 Apr 15;11(4):581. doi: 10.3390/biom11040581. Biomolecules. 2021. PMID: 33920974 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cell and molecular targeted therapies for diabetic retinopathy.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024 Jun 14;15:1416668. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1416668. eCollection 2024. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 38948520 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Drinking hydrogen water improves photoreceptor structure and function in retinal degeneration 6 mice.Sci Rep. 2022 Aug 10;12(1):13610. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-17903-8. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35948585 Free PMC article.
-
Retinal Ganglion Cell Transplantation: Approaches for Overcoming Challenges to Functional Integration.Cells. 2021 Jun 8;10(6):1426. doi: 10.3390/cells10061426. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34200991 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Flaxman SR, Bourne RRA, Resnikoff S, Ackland P, Braithwaite T, Cicinelli MV, Das A, Jonas JB, Keeffe J, Kempen JH, Leasher J, Limburg H, Naidoo K, Pesudovs K, Silvester A, Stevens GA, Tahhan N, Wong TY, Taylor HR. Global causes of blindness and distance vision impairment 1990–2020: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Glob Health. 2017;5:e1221–34. - PubMed
-
- Tham YC, Li X, Wong TY, Quigley HA, Aung T, Cheng CY. Global prevalence of glaucoma and projections of glaucoma burden through 2040: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Ophthalmology. 2014;121:2081–90. - PubMed
-
- Sommer A, Tielsch JM, Katz J, Quigley HA, Gottsch JD, Javitt J, Singh K. Relationship between intraocular pressure and primary open angle glaucoma among white and black Americans. The Baltimore Eye Survey. Arch Ophthalmol. 1991;109:1090–5. - PubMed
-
- Bergea B, Bodin L, Svedbergh B. Impact of intraocular pressure regulation on visual fields in open-angle glaucoma. Ophthalmology. 1999;106:997–1004. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

