Effects and Mechanisms of Electroacupuncture on Chronic Inflammatory Pain and Depression Comorbidity in Mice
- PMID: 32565863
- PMCID: PMC7275955
- DOI: 10.1155/2020/4951591
Effects and Mechanisms of Electroacupuncture on Chronic Inflammatory Pain and Depression Comorbidity in Mice
Abstract
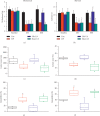
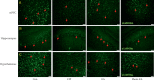
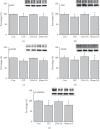
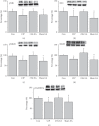
Comorbidity of chronic pain and major depression disorder (MDD) are common diseases. However, the mechanisms of electroacupuncture (EA) and the responses of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors in the brain remain unclear. Three injections of complete Freund's adjuvant (CFA) were administered to induce chronic inflammatory pain (CIP). EA was then performed once every other day from days 14 to 28. Behavior tests of chronic pain and depression were evaluated to make sure of the successful induction of comorbidity. We used Western blotting to analyze brain tissue from the prefrontal cortex (PFC), hippocampus, and hypothalamus for levels of phosphorylated N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor subunit 1 (pNR1), NR1, pNR2B, NR2B, and calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase type II alpha isoform (pCaMKIIα). The mechanical hyperalgesia, thermal hyperalgesia, and depression were observed in the CIP group. Furthermore, decreased levels of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors (NMDARs) were also noted. Not Sham EA but EA reversed chronic pain and depression as well as the decreased levels of NMDA in the signaling pathway. The CFA injections successfully induced a significant comorbidity model. EA treated the comorbidity by upregulating the NMDA signaling pathway in the PFC, hippocampus, and hypothalamus. Our results indicated significant mechanisms of comorbidity of chronic pain and MDD and EA-analgesia that involves the regulation of the NMDAR signaling pathway. These findings may be relevant to the evaluation and treatment of comorbidity of chronic pain and MDD.
Copyright © 2020 Hung-Yu Huang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no potential conflicts of interest from any commercial or financial relationships.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Synergistic antinociceptive effects of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor antagonist and electroacupuncture in the complete Freund's adjuvant-induced pain model.Int J Mol Med. 2011 Oct;28(4):669-75. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2011.728. Epub 2011 Jun 17. Int J Mol Med. 2011. PMID: 21687934
-
Electroacupuncture attenuates chronic inflammatory pain and depression comorbidity by inhibiting hippocampal neuronal apoptosis via the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway.Neurosci Lett. 2023 Aug 24;812:137411. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2023.137411. Epub 2023 Jul 27. Neurosci Lett. 2023. PMID: 37516346
-
Effects of electroacupuncture in a mouse model of fibromyalgia: role of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors and related mechanisms.Acupunct Med. 2017 Mar;35(1):59-68. doi: 10.1136/acupmed-2015-010986. Epub 2016 Jul 5. Acupunct Med. 2017. PMID: 27381504 Free PMC article.
-
Distal Electroacupuncture at the LI4 Acupoint Reduces CFA-Induced Inflammatory Pain via the Brain TRPV1 Signaling Pathway.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Sep 10;20(18):4471. doi: 10.3390/ijms20184471. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31510092 Free PMC article.
-
Electroacupuncture (EA) modulates the expression of NMDA receptors in primary sensory neurons in relation to hyperalgesia in rats.Brain Res. 2006 Nov 20;1120(1):46-53. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2006.08.077. Epub 2006 Sep 26. Brain Res. 2006. PMID: 17005164
Cited by
-
Acupuncture points injection mitigates chronic pain through transient receptor potential V1 in mice.Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2022 Apr;25(4):451-459. doi: 10.22038/IJBMS.2022.60121.13327. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2022. PMID: 35656078 Free PMC article.
-
Acupuncture for Chronic Pain-Related Depression: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Pain Res Manag. 2021 Feb 22;2021:6617075. doi: 10.1155/2021/6617075. eCollection 2021. Pain Res Manag. 2021. PMID: 33680223 Free PMC article.
-
TRPV1 Responses in the Cerebellum Lobules VI, VII, VIII Using Electroacupuncture Treatment for Chronic Pain and Depression Comorbidity in a Murine Model.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 May 10;22(9):5028. doi: 10.3390/ijms22095028. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34068557 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of acupuncture-electroacupuncture on inflammatory pain.Mol Pain. 2023 Jan-Dec;19:17448069231202882. doi: 10.1177/17448069231202882. Mol Pain. 2023. PMID: 37678839 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Accurate Chemogenetics Determines Electroacupuncture Analgesia Through Increased CB1 to Suppress the TRPV1 Pathway in a Mouse Model of Fibromyalgia.Life (Basel). 2025 May 20;15(5):819. doi: 10.3390/life15050819. Life (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40430245 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gaskin D. J. R. P. The Economic Costs of Pain in the United States. Washington, DC, USA: Institute of Medicine (US) Committee on Advancing Pain Research, Care, and Education; 2011. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK92521/
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

