In vitro and in vivo evaluation of the safety and efficacy of a novel liquid fiducial marker for image-guided radiotherapy
- PMID: 32565982
- PMCID: PMC7286123
- DOI: 10.3892/ol.2020.11591
In vitro and in vivo evaluation of the safety and efficacy of a novel liquid fiducial marker for image-guided radiotherapy
Abstract
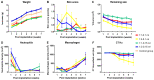
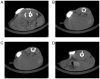
The true extent of a tumor is difficult to visualize, during radiotherapy, using current modalities. In the present study, the safety and feasibility of a mixture of N-butyl cyanoacrylate and lipiodol (NBCA/Lip) was evaluated in order to investigate the optimal combination for application as a fiducial marker for radiotherapy. Four combinations of NBCA/Lip injection (1:1-0.1, 1:1-0.15, 1:3-0.1 and 1:3-0.15 ml) were injected into the subcutaneous tissue of BALB/c mice. The changes in gross histopathology, body weight, skin score, marker volume, neutrophil and macrophage counts were observed to analyze the effects of the different mixing ratios and injection volumes, in order to identify the best combination. Evaluation according to the International Organization for Standardization criteria was further conducted in order to test the biocompatibility of the mixture, including an acute systematic assay with mice, cytotoxicity with L929 fibroblasts and delayed-type hypersensitivity tests with guinea pigs and an intradermal test with rabbits. The results revealed that at the seventh week, 42 markers (42/48; 87.5%) were still visible using computed tomography (CT) imaging. No serious adverse effects were observed throughout the study period; however, the combination of 1:1-0.1 ml had the lowest body weight and worst skin score. A review of the histopathological reaction to NBCA/Lip revealed a combination of acute inflammation, chronic inflammation, granulation tissue, foreign-body reaction and fibrous capsule formation. The 1:1 NBCA combination ratio resulted in the most intense tissue repair reaction and a slower degradation rate of markers. In general, the combination of 1:3-0.15 ml had a better fusion with local tissue, maintained a stable imaging nodule on CT images for 7 weeks and the final biocompatibility test demonstrated its safety. Overall, the findings of the present study demonstrated NBCA/Lip as a safe and feasible fiducial marker, when using the 1:3-0.15 ml combination.
Keywords: biocompatibility; esophageal cancer; image-guided radiotherapy; liquid fiducial marker; n-butyl cyanoacrylate.
Copyright: © Sun et al.
Figures


References
-
- Jin P, Van Der Horst A, De Jong R, van Hooft JE, Kamphuis M, van Wieringen N, Machiels M, Bel A, Hulshof MC, Alderliesten T. Marker-based quantification of interfractional tumor position variation and the use of markers for setup verification in radiation therapy for esophageal cancer. Radiother Oncol. 2015;117:412–418. doi: 10.1016/j.radonc.2015.10.005. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Machiels M, Van Hooft J, Jin P, van Berge Henegouwen MI, van Laarhoven HM, Alderliesten T, Hulshof MC. Endoscopy/EUS-guided fiducial marker placement in patients with esophageal cancer: A comparative analysis of 3 types of markers. Gastrointest Endosc. 2015;82:641–649. doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2015.03.1972. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
