Prevalence and Molecular Genetics of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Colonization in Nursing Homes in Saudi Arabia
- PMID: 32566056
- PMCID: PMC7290903
- DOI: 10.1155/2020/2434350
Prevalence and Molecular Genetics of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Colonization in Nursing Homes in Saudi Arabia
Abstract
Objective: Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) is one of the main causative agents of nosocomial infections that has posed a major threat to those with compromised immune systems such as nursing home residents. The aim of this study was to determine the rates of MRSA strains and the types of Staphylococcal Cassette Chromosome mec (SCCmec)in nursing homes in Saudi Arabia.
Methods: A total of 188 nasal swabs were collected from the residents and nursing staff in two nursing homes in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia. All MRSA isolates were tested for antimicrobial susceptibility and analyzed for mecA and SCCmec typing by multiplex PCR assay. Detection of the Panton-Valentine leukocidin (PVL) gene was also tested in all positive MRSA isolates by multiplex PCR using specific primers.
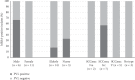
Results: Among the 188 collected nasal swabs (105 males and 83 females), MRSA colonization rate was 9.04% (11 (5.85%) females and 6 (5.71%) males). About 47% of MRSA were multidrug resistant (MDR) as acquired resistance to beta-lactam, macrolide, and aminoglycoside antibiotics. However, all the MRSA isolates showed susceptibility to vancomycin, tigecycline, and linezolid. All the MRSA isolates (n = 17) were mecA-positive with the SCCmec IVc (n = 7, 41.18%) as the most common SCCmec type followed by SCCmec V (n = 5, 29.41%) and SCCmec IVa (n = 2, 11.76%). The remaining isolates (n = 3) were nontypeable (17.65%). In addition, the PVL toxin gene was only detected in four of the male samples.
Conclusion: MRSA nasal colonization is a common incident among nursing home residents. The prevalence of community-associated (CA) MRSA (SCCmec IV and V) was more common than hospital-associated (HA) MRSA in our study samples. It is crucial to investigate such rate of incidence, which is a key tool in preventive medicine and would aid in determining health policy and predict emergent outbreaks.
Copyright © 2020 Ahmed Albarrag et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

