Curcumin, Alone or in Combination with Aminoguanidine, Increases Antioxidant Defenses and Glycation Product Detoxification in Streptozotocin-Diabetic Rats: A Therapeutic Strategy to Mitigate Glycoxidative Stress
- PMID: 32566072
- PMCID: PMC7260652
- DOI: 10.1155/2020/1036360
Curcumin, Alone or in Combination with Aminoguanidine, Increases Antioxidant Defenses and Glycation Product Detoxification in Streptozotocin-Diabetic Rats: A Therapeutic Strategy to Mitigate Glycoxidative Stress
Abstract
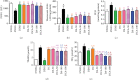
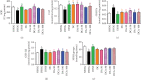
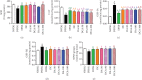
Both oxidative stress and the exacerbated generation of advanced glycation end products (AGEs) have crucial roles in the onset and progression of diabetic complications. Curcumin has antioxidant and antidiabetic properties; its combination with compounds capable of preventing the advanced glycation events, such as aminoguanidine, is an interesting therapeutic option to counteract diabetic complications. This study is aimed at investigating the effects of treatments with curcumin or aminoguanidine, alone or in combination, on metabolic alterations in streptozotocin-diabetic rats; the focus was mainly on the potential of these bioactive compounds to oppose the glycoxidative stress. Curcumin (90 mg/kg) or aminoguanidine (50 and 100 mg/kg), alone or in combination, slightly decreased glycemia and the biomarkers of early protein glycation, but markedly decreased AGE levels (biomarkers of advanced glycation) and oxidative damage biomarkers in the plasma, liver, and kidney of diabetic rats. Some novel insights about the in vivo effects of these bioactive compounds are centered on the triggering of cytoprotective machinery. The treatments with curcumin and/or aminoguanidine increased the activities of the antioxidant enzymes (paraoxonase 1, superoxide dismutase, and catalase) and the levels of AGE detoxification system components (AGE-R1 receptor and glyoxalase 1). In addition, combination therapy between curcumin and aminoguanidine effectively prevented dyslipidemia in diabetic rats. These findings demonstrate the combination of curcumin (natural antioxidant) and aminoguanidine (prototype therapeutic agent with anti-AGE activity) as a potential complementary therapeutic option for use with antihyperglycemic agents, which may aggregate beneficial effects against diabetic complications.
Copyright © 2020 Tayra Ferreira Oliveira Lima et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
Figures

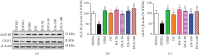


References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

