Massive atelectasis by mucoid impaction in an asthma patient during treatment with anti-interleukin-5 receptor antibody
- PMID: 32566229
- PMCID: PMC7300730
- DOI: 10.1002/rcr2.599
Massive atelectasis by mucoid impaction in an asthma patient during treatment with anti-interleukin-5 receptor antibody
Abstract
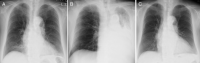
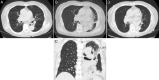
Benralizumab is an interleukin-5 (IL-5) receptor α-directed cytolytic monoclonal antibody that reduces rapid and nearly complete depletion of eosinophils by enhancing antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity. The depletion of eosinophilic inflammation is expected to reduce mucus hypersecretion and mucoid impaction. A 75-year-old non-smoking female had been treated for uncontrolled bronchial asthma with multiple drugs. Treatment with benralizumab was initiated after the asthma attack; however, four months later, she developed massive atelectasis in the left lung leading to the tracheal deviation, to the extent that nasal high-flow therapy was required. The laboratory data showed elevated neutrophil count, whereas blood eosinophils were almost completely depleted. The thick mucus was removed by bronchofiberscopy and the atelectasis was completely resolved. No exacerbation has been observed for nine months after discontinuation of benralizumab and initiation of erythromycin. This is the first documented case that developed atelectasis by mucoid impaction during treatment with anti-IL-5 receptor antibody.
Keywords: Asthma; atelectasis; benralizumab; interleukin‐5; mucus hypersecretion.
© 2020 The Authors. Respirology Case Reports published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd on behalf of The Asian Pacific Society of Respirology.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Ability of Serum IgE Concentration to Predict Exacerbation Risk and Benralizumab Efficacy for Patients with Severe Eosinophilic Asthma.Adv Ther. 2020 Feb;37(2):718-729. doi: 10.1007/s12325-019-01191-2. Epub 2019 Dec 14. Adv Ther. 2020. PMID: 31836949 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Benralizumab, an anti-interleukin 5 receptor α monoclonal antibody, versus placebo for uncontrolled eosinophilic asthma: a phase 2b randomised dose-ranging study.Lancet Respir Med. 2014 Nov;2(11):879-890. doi: 10.1016/S2213-2600(14)70201-2. Epub 2014 Oct 8. Lancet Respir Med. 2014. PMID: 25306557 Clinical Trial.
-
Spontaneous resolution of atopic dermatitis incidental to participation in benralizumab clinical trial for severe, uncontrolled asthma: a case report.J Med Case Rep. 2021 Mar 6;15(1):103. doi: 10.1186/s13256-021-02663-2. J Med Case Rep. 2021. PMID: 33673870 Free PMC article.
-
Safety of Eosinophil-Depleting Therapy for Severe, Eosinophilic Asthma: Focus on Benralizumab.Drug Saf. 2020 May;43(5):409-425. doi: 10.1007/s40264-020-00926-3. Drug Saf. 2020. PMID: 32242310 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Eosinophils, the IL-5/IL-5Rα axis, and the biologic effects of benralizumab in severe asthma.Respir Med. 2019 Nov-Dec;160:105819. doi: 10.1016/j.rmed.2019.105819. Epub 2019 Nov 11. Respir Med. 2019. PMID: 31734469 Review.
Cited by
-
Features of children with critical asthma hospitalized in a pediatric intensive care unit: Results from the ICU-3A study.Pediatr Pulmonol. 2025 Jan;60(1):e27322. doi: 10.1002/ppul.27322. Epub 2024 Oct 14. Pediatr Pulmonol. 2025. PMID: 39400483 Free PMC article.
-
Successful management of recurrent allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis after changing from mepolizumab to dupilumab: A case report.Respir Med Case Rep. 2022 Aug 17;39:101723. doi: 10.1016/j.rmcr.2022.101723. eCollection 2022. Respir Med Case Rep. 2022. PMID: 36043197 Free PMC article.
-
Improvement of Mucoid Impaction with Dupilumab in a Severe Asthma Patient.Maedica (Bucur). 2024 Jun;19(2):439-442. doi: 10.26574/maedica.2024.19.2.439. Maedica (Bucur). 2024. PMID: 39188820 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kolbeck R, Kozhich A, Koike M, et al. 2010. MEDI‐563, a humanized anti‐IL‐5 receptor alpha mAb with enhanced antibody‐dependent cell‐mediated cytotoxicity function. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 125(6):1344–1353. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

