Genome-wide characterization of the Zn(II)2Cys6 zinc cluster-encoding gene family in Pleurotus ostreatus and expression analyses of this family during developmental stages and under heat stress
- PMID: 32566411
- PMCID: PMC7295025
- DOI: 10.7717/peerj.9336
Genome-wide characterization of the Zn(II)2Cys6 zinc cluster-encoding gene family in Pleurotus ostreatus and expression analyses of this family during developmental stages and under heat stress
Abstract
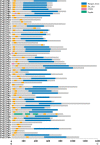
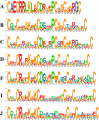
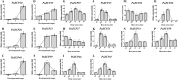
Pleurotus ostreatus is one of the most widely cultivated mushrooms in China. The regulatory mechanisms of fruiting body formation and the response to heat stress in P. ostreatus are main research focuses. The Zn(II)2Cys6 family is one of the largest families of transcriptional factors and plays important roles in multiple biological processes in fungi. In this study, we identified 66 zinc cluster proteins in P. ostreatus (PoZCPs) through a genome-wide search. The PoZCPs were classified into 15 types according to their zinc cluster domain. Physical and chemical property analyses showed a huge diversity among the PoZCPs. Phylogenetic analysis of PoZCPs classified these proteins into six groups and conserved motif combinations and similar gene structures were observed in each group. The expression profiles of these PoZCP genes during different developmental stages and under heat stress were further investigated by RNA-sequencing (RNA-seq), revealing diverse expression patterns. A total of 13 PoZCPs that may participate in development or the heat stress response were selected for validation of their expression levels through real-time quantitative PCR (RT-qPCR) analysis, and some developmental stage-specific and heat stress-responsive candidates were identified. The findings contribute to our understanding of the roles and regulatory mechanisms of ZCPs in P. ostreatus.
Keywords: Fruiting body development; Heat stress; Pleurotus ostreatus; Zinc cluster protein.
© 2020 Hou et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Genome-wide analysis of bZIP gene family members in Pleurotus ostreatus, and potential roles of PobZIP3 in development and the heat stress response.Microb Biotechnol. 2024 Feb;17(2):e14413. doi: 10.1111/1751-7915.14413. Microb Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 38376071 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-Wide Characterization and Expression Analyses of Pleurotus ostreatus MYB Transcription Factors during Developmental Stages and under Heat Stress Based on de novo Sequenced Genome.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Jul 14;19(7):2052. doi: 10.3390/ijms19072052. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30011913 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide identification and expression analyses of C2H2 zinc finger transcription factors in Pleurotus ostreatus.PeerJ. 2022 Jan 5;10:e12654. doi: 10.7717/peerj.12654. eCollection 2022. PeerJ. 2022. PMID: 35036086 Free PMC article.
-
Expression patterns of two pal genes of Pleurotus ostreatus across developmental stages and under heat stress.BMC Microbiol. 2019 Oct 26;19(1):231. doi: 10.1186/s12866-019-1594-4. BMC Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31655558 Free PMC article.
-
Evolution of a fungal regulatory gene family: the Zn(II)2Cys6 binuclear cluster DNA binding motif.Fungal Genet Biol. 1997 Jun;21(3):388-405. doi: 10.1006/fgbi.1997.0993. Fungal Genet Biol. 1997. PMID: 9290251 Review.
Cited by
-
Gene age shapes the transcriptional landscape of sexual morphogenesis in mushroom-forming fungi (Agaricomycetes).Elife. 2022 Feb 14;11:e71348. doi: 10.7554/eLife.71348. Elife. 2022. PMID: 35156613 Free PMC article.
-
Lessons on fruiting body morphogenesis from genomes and transcriptomes of Agaricomycetes.Stud Mycol. 2023 Jul;104:1-85. doi: 10.3114/sim.2022.104.01. Epub 2023 Jan 31. Stud Mycol. 2023. PMID: 37351542 Free PMC article.
-
Integrated transcriptome and proteome analysis reveals molecular responses of soybean anther under high-temperature stress.Front Plant Sci. 2023 Jun 14;14:1187922. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2023.1187922. eCollection 2023. Front Plant Sci. 2023. PMID: 37389300 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide analysis of bZIP gene family members in Pleurotus ostreatus, and potential roles of PobZIP3 in development and the heat stress response.Microb Biotechnol. 2024 Feb;17(2):e14413. doi: 10.1111/1751-7915.14413. Microb Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 38376071 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide identification and expression analysis revealed key transcription factors as potential regulators of high-temperature adaptation of Coriolopsis trogii.Arch Microbiol. 2024 Jul 19;206(8):357. doi: 10.1007/s00203-024-04081-6. Arch Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39028428
References
-
- Arroyo-Herrera A, Figueroa-Yáñez L, Castano E, Santamaría J, Pereira-Santana A, Espadas-Alcocer J, Sánchez-Teyer F, Espadas-Gil F, Alcaraz LD, López-Gómez R. A novel Dreb2-type gene from Carica papaya confers tolerance under abiotic stress. Plant Cell, Tissue and Organ Culture (PCTOC) 2016;125(1):119–133. doi: 10.1007/s11240-015-0934-9. - DOI
-
- Cai HY, Yang S, Yan Y, Xiao ZL, Cheng JB, Wu J, Qiu AL, Lai Y, Mou SL, Guan DY. CaWRKY6 transcriptionally activates CaWRKY40, regulates Ralstonia solanacearum resistance, and confers high-temperature and high-humidity tolerance in pepper. Journal of Experimental Botany. 2015;66(11):3163–3174. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erv125. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

