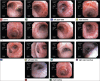
Diffuse Endobronchial Telangiectasia
- PMID: 32566532
- PMCID: PMC7289210
- DOI: 10.4103/ijabmr.IJABMR_343_18
Diffuse Endobronchial Telangiectasia
Abstract
Hemoptysis is one of the most common reasons for seeking emergency care. Infections and malignancy are the leading causes of hemoptysis although caused by various other pulmonary and extrapulmonary conditions. Most causes are self-limiting and do not warrant any aggressive investigation. Endobronchial telangiectasia can rarely cause hemoptysis and is seen in patients with hemorrhagic hereditary telangiectasia or scleroderma. Isolated diffuse endobronchial telangiectasia is rare and is only reported in one case in literature. We present another case of diffuse endobronchial telangiectasia in a young adult who presented with recurrent hemoptysis. Computer tomography scan was normal, but bronchoscopy showed multiple endobronchial arteriovenous malformations in the entire tracheobronchial tree.
Keywords: Arteriovenous malformations; endobronchial telangiectasia; hemoptysis.
Copyright: © 2020 International Journal of Applied and Basic Medical Research.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Cardenas-Garcia J, Feller-Kopman D. POINT: Should all initial episodes of hemoptysis be evaluated by bronchoscopy? Yes. Chest. 2018;153:302–5. - PubMed
-
- Mondoni M, Carlucci P, Cipolla G, Fois A, Gasparini S, Marani S, et al. Bronchoscopy in Patients with hemoptysis and negative imaging tests. Chest. 2018;153:1510–1. - PubMed
-
- Loewen AH, Kelly MM, Tremblay A. Endobronchial telangiectasias. J Bronchology Interv Pulmonol. 2006;13:210–1.
-
- Lincoln MJ, Shigeoka JW. Pulmonary telangiectasia without hypoxemia. Chest. 1988;93:1097–8. - PubMed
-
- Kim JH, Follett JV, Rice JR, Hampson NB. Endobronchial telangiectasias and hemoptysis in scleroderma. Am J Med. 1988;84:173–4. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources