Macrolide-Resistant Mycoplasma pneumoniae Infections in Pediatric Community-Acquired Pneumonia
- PMID: 32568052
- PMCID: PMC7323531
- DOI: 10.3201/eid2607.200017
Macrolide-Resistant Mycoplasma pneumoniae Infections in Pediatric Community-Acquired Pneumonia
Abstract
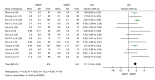
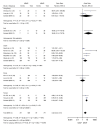
A high prevalence rate of macrolide-resistant Mycoplasma pneumoniae (MRMP) has been reported in Asia. We performed a systematic review and meta-analysis to investigate the effect of macrolide resistance on the manifestations and clinical judgment during M. pneumoniae infections. We found no difference in clinical severity between MRMP and macrolide-sensitive Mycoplasma pneumoniae (MSMP) infections. However, in the pooled data, patients infected with MRMP had a longer febrile period (1.71 days), length of hospital stay (1.61 day), antibiotic drug courses (2.93 days), and defervescence time after macrolide treatment (2.04 days) compared with patients infected with MSMP. The risk of fever lasting for >48 hours after macrolide treatment was also significantly increased (OR 21.24), and an increased proportion of patients was changed to second-line treatment (OR 4.42). Our findings indicate diagnostic and therapeutic challenges after the emergence of MRMP. More precise diagnostic tools and clearly defined treatment should be appraised in the future.
Keywords: Asia; Mycoplasma pneumoniae; antimicrobial resistance; bacteria; children; macrolide resistance; pneumonia.
Figures
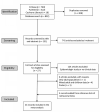


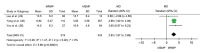
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

