A Social Media Study on the Associations of Flavored Electronic Cigarettes With Health Symptoms: Observational Study
- PMID: 32568093
- PMCID: PMC7338924
- DOI: 10.2196/17496
A Social Media Study on the Associations of Flavored Electronic Cigarettes With Health Symptoms: Observational Study
Abstract
Background: In recent years, flavored electronic cigarettes (e-cigarettes) have become popular among teenagers and young adults. Discussions about e-cigarettes and e-cigarette use (vaping) experiences are prevalent online, making social media an ideal resource for understanding the health risks associated with e-cigarette flavors from the users' perspective.
Objective: This study aimed to investigate the potential associations between electronic cigarette liquid (e-liquid) flavors and the reporting of health symptoms using social media data.
Methods: A dataset consisting of 2.8 million e-cigarette-related posts was collected using keyword filtering from Reddit, a social media platform, from January 2013 to April 2019. Temporal analysis for nine major health symptom categories was used to understand the trend of public concerns related to e-cigarettes. Sentiment analysis was conducted to obtain the proportions of positive and negative sentiment scores for all reported health symptom categories. Topic modeling was applied to reveal the topics related to e-cigarettes and health symptoms. Furthermore, generalized estimating equation (GEE) models were used to quantitatively measure potential associations between e-liquid flavors and the reporting of health symptoms.
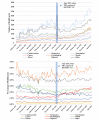
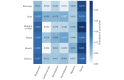
Results: Temporal analysis showed that the Respiratory category was consistently the most discussed health symptom category among all categories related to e-cigarettes on Reddit, followed by the Throat category. Sentiment analysis showed higher proportions of positive sentiment scores for all reported health symptom categories, except for the Cancer category. Topic modeling conducted on all health-related posts showed that 17 of the top 100 topics were flavor related. GEE models showed different associations between the reporting of health symptoms and e-liquid flavor categories, for example, lower association of the Beverage flavors with Respiratory compared with other flavors and higher association of the Fruit flavors with Cardiovascular than other flavors.
Conclusions: This study identified different potential associations between e-liquid flavors and the reporting of health symptoms using social media data. The results of this study provide valuable information for further investigation of the health effects associated with different e-liquid flavors.
Keywords: e-cigarette; eHealth; social media.
©Long Chen, Xinyi Lu, Jianbo Yuan, Joyce Luo, Jiebo Luo, Zidian Xie, Dongmei Li. Originally published in the Journal of Medical Internet Research (http://www.jmir.org), 22.06.2020.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: None declared.
Figures
Similar articles
-
User Perceptions of Different Electronic Cigarette Flavors on Social Media: Observational Study.J Med Internet Res. 2020 Jun 24;22(6):e17280. doi: 10.2196/17280. J Med Internet Res. 2020. PMID: 32579123 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of symptoms and their potential associations with e-liquids' components: a social media study.BMC Public Health. 2016 Jul 30;16:674. doi: 10.1186/s12889-016-3326-0. BMC Public Health. 2016. PMID: 27475060 Free PMC article.
-
Public Reactions to the New York State Policy on Flavored Electronic Cigarettes on Twitter: Observational Study.JMIR Public Health Surveill. 2022 Feb 3;8(2):e25216. doi: 10.2196/25216. JMIR Public Health Surveill. 2022. PMID: 35113035 Free PMC article.
-
[Harmful health effects of flavors in e-cigarettes].Laryngorhinootologie. 2025 May;104(5):288-295. doi: 10.1055/a-2341-0544. Epub 2024 Jul 12. Laryngorhinootologie. 2025. PMID: 38996433 Review. German.
-
History repeats itself: Role of characterizing flavors on nicotine use and abuse.Neuropharmacology. 2020 Oct 15;177:108162. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2020.108162. Epub 2020 Jun 1. Neuropharmacology. 2020. PMID: 32497589 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Monitoring and Identifying Emerging e-Cigarette Brands and Flavors on Twitter: Observational Study.JMIR Form Res. 2022 Dec 5;6(12):e42241. doi: 10.2196/42241. JMIR Form Res. 2022. PMID: 36469415 Free PMC article.
-
e-Cigarette Tobacco Flavors, Public Health, and Toxicity: Narrative Review.Online J Public Health Inform. 2024 May 27;16:e51991. doi: 10.2196/51991. Online J Public Health Inform. 2024. PMID: 38801769 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Perception of the Food and Drug Administration Electronic Cigarette Flavor Enforcement Policy on Twitter: Observational Study.JMIR Public Health Surveill. 2022 Mar 29;8(3):e25697. doi: 10.2196/25697. JMIR Public Health Surveill. 2022. PMID: 35348461 Free PMC article.
-
Community and Opinion Leadership Effects on Vaping Discourse: A Network Analysis of Online Reddit Threads.J Health Commun. 2023 Aug 3;28(8):487-497. doi: 10.1080/10810730.2023.2225447. Epub 2023 Jun 21. J Health Commun. 2023. PMID: 37341521 Free PMC article.
-
Potential Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic on Public Perception of Water Pipes on Reddit: Observational Study.JMIR Infodemiology. 2023 Apr 20;3:e40913. doi: 10.2196/40913. eCollection 2023. JMIR Infodemiology. 2023. PMID: 37124245 Free PMC article.
References
-
- US Department of Health and Human Services. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. National Center for Chronic Disease Prevention and Health Promotion . e-Cigarette Use Among Youth and Young Adults: A Report of the Surgeon General. Atlanta, GA: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention; 2016.
-
- Rachel G, Neal B, Stanton G. Center for Tobacco Control Research and Education. 2013. [2020-05-07]. Background Paper on E-cigarettes (Electronic Nicotine Delivery Systems) https://escholarship.org/uc/item/13p2b72n.
-
- Hsu G, Sun J, Zhu S. Evolution of electronic cigarette brands from 2013-2014 to 2016-2017: analysis of brand websites. J Med Internet Res. 2018 Mar 12;20(3):e80. doi: 10.2196/jmir.8550. https://www.jmir.org/2018/3/e80/ - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Schneller LM, Bansal-Travers M, Goniewicz ML, McIntosh S, Ossip D, O'Connor RJ. Use of flavored electronic cigarette refill liquids among adults and youth in the US-results from wave 2 of the population assessment of tobacco and health study (2014-2015) PLoS One. 2018;13(8):e0202744. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0202744. http://dx.plos.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0202744 - DOI - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

