Operating Protocols of a Community Treatment Center for Isolation of Patients with Coronavirus Disease, South Korea
- PMID: 32568665
- PMCID: PMC7510742
- DOI: 10.3201/eid2610.201460
Operating Protocols of a Community Treatment Center for Isolation of Patients with Coronavirus Disease, South Korea
Abstract
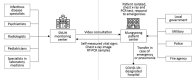
Most persons with confirmed coronavirus disease (COVID-19) have no or mild symptoms. During the COVID-19 pandemic, communities need efficient methods to monitor asymptomatic patients to reduce transmission. We describe the structure and operating protocols of a community treatment center (CTC) run by Seoul National University Hospital (SNUH) in South Korea. SNUH converted an existing facility into a CTC to isolate patients who had confirmed COVID-19 but mild or no symptoms. Patients reported self-measured vital signs and symptoms twice a day by using a smartphone application. Medical staff in a remote monitoring center at SNUH reviewed patient vital signs and provided video consultation to patients twice daily. The CTC required few medical staff to perform medical tests, monitor patients, and respond to emergencies. During March 5-26, 2020, we admitted and treated 113 patients at this center. CTCs could be an alternative to hospital admission for isolating patients and preventing community transmission.
Keywords: 2019 novel coronavirus disease; COVID-19; CTC; SARS; SARS-CoV-2; South Korea; community treatment center; coronavirus; coronavirus disease; quarantine facility; respiratory infections; severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2; viruses; zoonoses.
Figures


References
-
- Kinross P, Suetens C, Gomes Dias J, Alexakis L, Wijermans A, Colzani E, et al.; ECDC Public Health Emergency Team. Rapidly increasing cumulative incidence of coronavirus disease (COVID-19) in the European Union/European Economic Area and the United Kingdom, 1 January to 15 March 2020. Euro Surveill. 2020;25:2000285. 10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2020.25.11.2000285 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lai CC, Wang CY, Wang YH, Hsueh SC, Ko WC, Hsueh PR. Global epidemiology of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): disease incidence, daily cumulative index, mortality, and their association with country healthcare resources and economic status. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2020;55:105946. 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.105946 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

