Automated detection of COVID-19 cases using deep neural networks with X-ray images
- PMID: 32568675
- PMCID: PMC7187882
- DOI: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2020.103792
Automated detection of COVID-19 cases using deep neural networks with X-ray images
Abstract
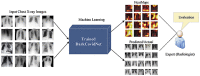
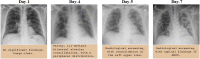
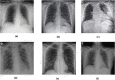
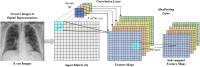
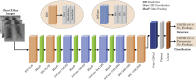
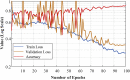
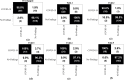
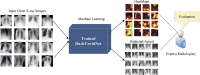
The novel coronavirus 2019 (COVID-2019), which first appeared in Wuhan city of China in December 2019, spread rapidly around the world and became a pandemic. It has caused a devastating effect on both daily lives, public health, and the global economy. It is critical to detect the positive cases as early as possible so as to prevent the further spread of this epidemic and to quickly treat affected patients. The need for auxiliary diagnostic tools has increased as there are no accurate automated toolkits available. Recent findings obtained using radiology imaging techniques suggest that such images contain salient information about the COVID-19 virus. Application of advanced artificial intelligence (AI) techniques coupled with radiological imaging can be helpful for the accurate detection of this disease, and can also be assistive to overcome the problem of a lack of specialized physicians in remote villages. In this study, a new model for automatic COVID-19 detection using raw chest X-ray images is presented. The proposed model is developed to provide accurate diagnostics for binary classification (COVID vs. No-Findings) and multi-class classification (COVID vs. No-Findings vs. Pneumonia). Our model produced a classification accuracy of 98.08% for binary classes and 87.02% for multi-class cases. The DarkNet model was used in our study as a classifier for the you only look once (YOLO) real time object detection system. We implemented 17 convolutional layers and introduced different filtering on each layer. Our model (available at (https://github.com/muhammedtalo/COVID-19)) can be employed to assist radiologists in validating their initial screening, and can also be employed via cloud to immediately screen patients.
Keywords: Chest X-ray images; Coronavirus (COVID-19); Deep learning; Radiology images.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


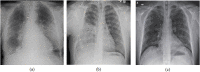
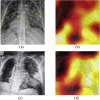
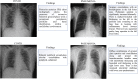
References
-
- World Health Organization . World Health Organization (WHO); 2020. Pneumonia of Unknown Cause–China. Emergencies Preparedness, Response, Disease Outbreak News.
-
- Wu Z., McGoogan J.M. Characteristics of and important lessons from the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak in China: summary of a report of 72 314 cases from the Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention. Jama. 2020;323(13):1239–1242. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

