Feasibility and physiological effects of prone positioning in non-intubated patients with acute respiratory failure due to COVID-19 (PRON-COVID): a prospective cohort study
- PMID: 32569585
- PMCID: PMC7304954
- DOI: 10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30268-X
Feasibility and physiological effects of prone positioning in non-intubated patients with acute respiratory failure due to COVID-19 (PRON-COVID): a prospective cohort study
Abstract
Background: The COVID-19 pandemic is challenging advanced health systems, which are dealing with an overwhelming number of patients in need of intensive care for respiratory failure, often requiring intubation. Prone positioning in intubated patients is known to reduce mortality in moderate-to-severe acute respiratory distress syndrome. We aimed to investigate feasibility and effect on gas exchange of prone positioning in awake, non-intubated patients with COVID-19-related pneumonia.
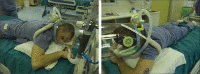
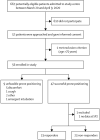
Methods: In this prospective, feasibility, cohort study, patients aged 18-75 years with a confirmed diagnosis of COVID-19-related pneumonia receiving supplemental oxygen or non-invasive continuous positive airway pressure were recruited from San Gerardo Hospital, Monza, Italy. We collected baseline data on demographics, anthropometrics, arterial blood gas, and ventilation parameters. After baseline data collection, patients were helped into the prone position, which was maintained for a minimum duration of 3 h. Clinical data were re-collected 10 min after prone positioning and 1 h after returning to the supine position. The main study outcome was the variation in oxygenation (partial pressure of oxygen [PaO2]/fractional concentration of oxygen in inspired air [FiO2]) between baseline and resupination, as an index of pulmonary recruitment. This study is registered on ClinicalTrials.gov, NCT04365959, and is now complete.
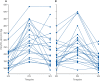
Findings: Between March 20 and April 9, 2020, we enrolled 56 patients, of whom 44 (79%) were male; the mean age was 57·4 years (SD 7·4) and the mean BMI was 27·5 kg/m2 (3·7). Prone positioning was feasible (ie, maintained for at least 3 h) in 47 patients (83·9% [95% CI 71·7 to 92·4]). Oxygenation substantially improved from supine to prone positioning (PaO2/FiO2 ratio 180·5 mm Hg [SD 76·6] in supine position vs 285·5 mm Hg [112·9] in prone position; p<0·0001). After resupination, improved oxygenation was maintained in 23 patients (50·0% [95% CI 34·9-65·1]; ie, responders); however, this improvement was on average not significant compared with before prone positioning (PaO2/FiO2 ratio 192·9 mm Hg [100·9] 1 h after resupination; p=0·29). Patients who maintained increased oxygenation had increased levels of inflammatory markers (C-reactive protein: 12·7 mg/L [SD 6·9] in responders vs 8·4 mg/L [6·2] in non-responders; and platelets: 241·1 × 103/μL [101·9] vs 319·8 × 103/μL [120·6]) and shorter time between admission to hospital and prone positioning (2·7 days [SD 2·1] in responders vs 4·6 days [3·7] in non-responders) than did those for whom improved oxygenation was not maintained. 13 (28%) of 46 patients were eventually intubated, seven (30%) of 23 responders and six (26%) of 23 non-responders (p=0·74). Five patients died during follow-up due to underlying disease, unrelated to study procedure.
Interpretation: Prone positioning was feasible and effective in rapidly ameliorating blood oxygenation in awake patients with COVID-19-related pneumonia requiring oxygen supplementation. The effect was maintained after resupination in half of the patients. Further studies are warranted to ascertain the potential benefit of this technique in improving final respiratory and global outcomes.
Funding: University of Milan-Bicocca.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
Comment in
-
Prone positioning in non-intubated patients with COVID-19: raising the bar.Lancet Respir Med. 2020 Aug;8(8):744-745. doi: 10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30269-1. Epub 2020 Jun 19. Lancet Respir Med. 2020. PMID: 32569584 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

