Application of cognitive Internet of Medical Things for COVID-19 pandemic
- PMID: 32570016
- PMCID: PMC7287427
- DOI: 10.1016/j.dsx.2020.06.014
Application of cognitive Internet of Medical Things for COVID-19 pandemic
Abstract
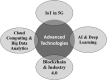
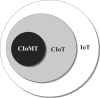
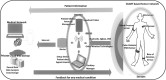
Background and aim: In the age of advanced digital technology, smart healthcare based on the Internet of Things (IoT) is gaining importance to deal with the current COVID-19 pandemic. In this paper, the novel application of cognitive radio (CR) based IoT specific for the medical domain referred to as Cognitive Internet of Medical Things (CIoMT) is explored to tackle the global challenge. This concept of CIoT is best suited to this pandemic as every person is to be connected and monitored through a massive network that requires efficient spectrum management.
Methods: An extensive literature survey is conducted in the Google Scholar, Scopus, PubMed, Research Gate, and IEEE Xplore databases using the terms "COVID-19" and "Cognitive IoT" or "Corona virus" and "IoMT". The latest data and inputs from official websites and reports are used for further investigation and analysis of the application areas.
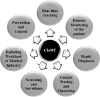
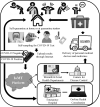
Results: This review encompasses different novel applications of CIoMT for fighting the ongoing COVID-19 health crisis. The CR based dynamic spectrum allocation technique is the solution for accommodating a massive number of devices and a wide number of applications. The CIoMT platform enables real-time tracking, remote health monitoring, rapid diagnosis of the cases, contact tracking, clustering, screening, and surveillance thus, reducing the workload on the medical industry for prevention and control of the infection. The challenges and future research directions are also identified.
Conclusions: CIoMT is a promising technology for rapid diagnosis, dynamic monitoring and tracking, better treatment and control without spreading the virus to others.
Keywords: COVID-19; Cognitive Internet of Medical Things (CIoMT); Coronavirus; Internet of Things (IoT).
Copyright © 2020 Diabetes India. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- https://www.worldometers.info/coronavirus/ Accessed on 25th May.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

