Cultivation of Mushrooms and Their Lignocellulolytic Enzyme Production Through the Utilization of Agro-Industrial Waste
- PMID: 32570772
- PMCID: PMC7355594
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules25122811
Cultivation of Mushrooms and Their Lignocellulolytic Enzyme Production Through the Utilization of Agro-Industrial Waste
Abstract
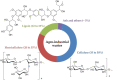
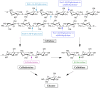
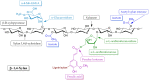
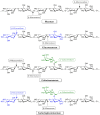
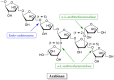
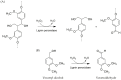
A large amount of agro-industrial waste is produced worldwide in various agricultural sectors and by different food industries. The disposal and burning of this waste have created major global environmental problems. Agro-industrial waste mainly consists of cellulose, hemicellulose and lignin, all of which are collectively defined as lignocellulosic materials. This waste can serve as a suitable substrate in the solid-state fermentation process involving mushrooms. Mushrooms degrade lignocellulosic substrates through lignocellulosic enzyme production and utilize the degraded products to produce their fruiting bodies. Therefore, mushroom cultivation can be considered a prominent biotechnological process for the reduction and valorization of agro-industrial waste. Such waste is generated as a result of the eco-friendly conversion of low-value by-products into new resources that can be used to produce value-added products. Here, we have produced a brief review of the current findings through an overview of recently published literature. This overview has focused on the use of agro-industrial waste as a growth substrate for mushroom cultivation and lignocellulolytic enzyme production.
Keywords: lignocellulolytic enzymes; lignocellulosic materials; mushroom cultivation; solid state fermentation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Mirabella N., Castellani V., Sala S. Current options for the valorization of food manufacturing waste: A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2014;65:28–41. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2013.10.051. - DOI
-
- Sadh P.K., Duhan S., Duhan J.S. Agro-industrial wastes and their utilization using solid state fermentation: A review. Bioresour. Bioprocess. 2018;5:1. doi: 10.1186/s40643-017-0187-z. - DOI
-
- Panesar P.S., Kaur R., Singla G., Sangwan R.S. Bio-processing of agro-industrial wastes for production of food-grade enzymes: Progress and prospects. Appl. Food Biotechnol. 2016;3:4.
-
- Anwar Z., Gulfraz M., Irshad M. Agro-industrial lignocellulosic biomass a key to unlock the future bio-energy: A brief review. J. Radiat. Res. Appl. Sc. 2014;7:163–173. doi: 10.1016/j.jrras.2014.02.003. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

