Systemic lupus erythematosus, lupus nephritis and end-stage renal disease: a pragmatic review mapping disease severity and progression
- PMID: 32571142
- PMCID: PMC7425376
- DOI: 10.1177/0961203320932219
Systemic lupus erythematosus, lupus nephritis and end-stage renal disease: a pragmatic review mapping disease severity and progression
Abstract
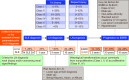
Objective: The understanding of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and lupus nephritis (LN) pathogenesis remains incomplete. This review assessed LN development in SLE, within-LN progression and progression to end-stage renal disease (ESRD).
Methods: A keyword-based literature search was conducted, and 26 publications were included.
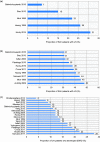
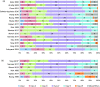
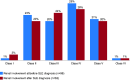
Results: Overall, 7-31% of patients had LN at SLE diagnosis; 31-48% developed LN after SLE diagnosis, most within 5 years. Class IV was the most commonly found LN class and had the worst prognosis. Histological transformation occurred in 40-76% of patients, more frequently from non-proliferative rather than proliferative lesions. Cumulative 5- and 10-year ESRD incidences in patients with SLE were 3% and 4%, respectively, and 3-11% and 6-19%, respectively, in patients with SLE and LN.
Conclusions: Elevated serum creatinine was identified as a predictor of worsening disease state, and progression within LN classes and from SLE/LN to ESRD. This review highlights the substantial risk for developing LN and progressing to ESRD amongst patients with SLE.
Keywords: Nephritis; renal lupus; systemic lupus erythematosus.
Figures
References
-
- Ines L, Silva C, Galindo M, et al. Classification of systemic lupus erythematosus: Systemic Lupus International Collaborating Clinics versus American College of Rheumatology Criteria. A comparative study of 2,055 patients from a real-life, international systemic lupus erythematosus cohort. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken) 2015; 67: 1180–1185. - PubMed
-
- Beckwith H, Lightstone L. Rituximab in systemic lupus erythematosus and lupus nephritis. Nephron Clin Pract 2014; 128: 250–254. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

