Very high baseline HIV viremia impairs efficacy of non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor-based ART: a long-term observation in treatment-naïve patients
- PMID: 32571409
- PMCID: PMC7310120
- DOI: 10.1186/s40249-020-00700-8
Very high baseline HIV viremia impairs efficacy of non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor-based ART: a long-term observation in treatment-naïve patients
Abstract
Background: It is not completely clear whether a very high pre-therapy viral load (≥ 500 000 copies/ml) can impair the virological response. The aim of this study was to examine the influence of very high baseline HIV-RNA levels on long-term virological responses under one type of regimen.
Methods: A retrospective study was performed based on data from two multicenter cohorts in China from January to November 2009, and from May 2013 to December 2015. Untreated HIV infected adults between 18 and 65 years old were recruited before receiving non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor-based regimen. All patients had baseline HIV-RNA levels over 500 copies/ml, good adherence, and were followed for at least 24 weeks. Virological suppression was defined as the first HIV-RNA < 50 copies/ml. Virological failure was defined as any of incomplete viral suppression (HIV-RNA ≥ 200 copies/ml without virological suppression within 24 weeks of treatment) and viral rebound (confirmed HIV-RNA level ≥ 50 copies/ml after virological suppression). Chi-square test, Kaplan-Meier analysis, Cox proportional hazards model and Logistic regression were used to compare virological response between each pretreated viral load stratum.
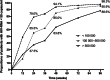
Results: A total of 758 treatment-naïve HIV patients in China were enlisted. Median follow-up time (IQR) was 144 (108-276) weeks. By week 48, rates of virological suppression in three groups (< 100 000, 100 000-500 000 and ≥ 500 000 copies/ml) were 94.1, 85.0, and 63.8%, respectively (P < 0.001). Very high baseline HIV viremia over 500 000 copies/ml were found to be associated with delayed virological suppression (≥ 500 000 vs < 100 000, adjusted relative hazard = 0.455, 95% CI: 0.32-0.65; P < 0.001) as well as incomplete viral suppression (≥ 500 000 vs < 100 000, adjusted odds ratio [aOR] = 6.084, 95% CI: 2.761-13.407; P < 0.001) and viral rebound (≥ 50 000 vs < 100 000, aOR = 3.671, 95% CI: 1.009-13.355, P = 0.048).
Conclusions: Very high levels of pre-treatment HIV-RNA were related with delayed efficacy of NNRTI-based ART and increased risk of treatment failure. More potent initial regimens should be considered for those with this clinical character.
Keywords: Antiretroviral therapy; Baseline RNA; HIV; Treatment outcome; Viral load; Virologic response.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest related to this study.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Time spent with residual viraemia after virological suppression below 50 HIV-RNA copies/mL according to type of first-line antiretroviral regimen.Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2018 Oct;52(4):492-499. doi: 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2018.07.001. Epub 2018 Sep 13. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2018. PMID: 30009958
-
Virological suppression and clinical management in response to viremia in South African HIV treatment program: A multicenter cohort study.PLoS Med. 2020 Feb 25;17(2):e1003037. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1003037. eCollection 2020 Feb. PLoS Med. 2020. PMID: 32097428 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of low-level viraemia on virological failure among Asian children with perinatally acquired HIV on first-line combination antiretroviral treatment: a multicentre, retrospective cohort study.J Int AIDS Soc. 2020 Jul;23(7):e25550. doi: 10.1002/jia2.25550. J Int AIDS Soc. 2020. PMID: 32628816 Free PMC article.
-
[Data on rilpivirine in treatment-naïve patients. Lessons from ECHO, THRIVE and STaR].Enferm Infecc Microbiol Clin. 2013 Jun;31 Suppl 2:20-9. doi: 10.1016/S0213-005X(13)70139-3. Enferm Infecc Microbiol Clin. 2013. PMID: 24252530 Review. Spanish.
-
Molecular biological assessment methods and understanding the course of the HIV infection.APMIS Suppl. 2003;(114):1-37. APMIS Suppl. 2003. PMID: 14626050 Review.
Cited by
-
The prevalence of low-level viraemia and its association with virological failure in people living with HIV: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Emerg Microbes Infect. 2025 Dec;14(1):2447613. doi: 10.1080/22221751.2024.2447613. Epub 2025 Jan 8. Emerg Microbes Infect. 2025. PMID: 39727007 Free PMC article.
-
Higher Risk of Mortality and Virologic Failure in HIV-Infected Patients With High Viral Load at Antiretroviral Therapy Initiation: An Observational Cohort Study in Chongqing, China.Front Public Health. 2022 Feb 3;10:800839. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.800839. eCollection 2022. Front Public Health. 2022. PMID: 35186841 Free PMC article.
-
Early on-treatment plasma interleukin-18 as a promising indicator for long-term virological response in patients with HIV-1 infection.Front Med (Lausanne). 2023 Jun 13;10:1170208. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2023.1170208. eCollection 2023. Front Med (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 37384047 Free PMC article.
-
HIV Virologic Failure among Patients with Persistent Low-Level Viremia in Nairobi, Kenya: It Is Time to Review the >1000 Virologic Failure Threshold.Biomed Res Int. 2023 Apr 27;2023:8961372. doi: 10.1155/2023/8961372. eCollection 2023. Biomed Res Int. 2023. PMID: 37152588 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and safety of ainuovirine versus efavirenz combination therapies with lamivudine/tenofovir disoproxil fumarate for medication of treatment-naïve HIV-1-positive adults: week 48 results of a randomized controlled phase 3 clinical trial followed by an open-label setting until week 96.Lancet Reg Health West Pac. 2023 Apr 24;36:100769. doi: 10.1016/j.lanwpc.2023.100769. eCollection 2023 Jul. Lancet Reg Health West Pac. 2023. PMID: 37547039 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Egger M, May M, Chene G, Phillips AN, Ledergerber B, Dabis F, et al. Prognosis of HIV-1-infected patients starting highly active antiretroviral therapy: a collaborative analysis of prospective studies. Lancet. 2002;360(9327):119–129. - PubMed
-
- Palella FJ, Jr, Delaney KM, Moorman AC, Loveless MO, Fuhrer J, Satten GA, et al. Declining morbidity and mortality among patients with advanced human immunodeficiency virus infection. HIV outpatient study investigators. N Engl J Med. 1998;338(13):853–860. - PubMed
-
- Wood E, Hogg RS, Yip B, Quercia R, Harrigan PR, O'Shaughnessy MV, et al. Higher baseline levels of plasma human immunodeficiency virus type 1 RNA are associated with increased mortality after initiation of triple-drug antiretroviral therapy. J Infect Dis. 2003;188(10):1421–1425. - PubMed
-
- Wood E, Hogg RS, Yip B, Harrigan PR, Montaner JS. Why are baseline HIV RNA levels 100,000 copies/mL or greater associated with mortality after the initiation of antiretroviral therapy? J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2005;38(3):289–295. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 2017ZX10202101/National Key Technologies R&D Program for the 13th Five-Year Plan
- 2012ZX10001003-001/the National Key Technologies R&D Program for the 12th Five-Year Plan
- 2008ZX10001006-001/the National Key Technologies R&D Program for the 11th Five-Year Plan
- CAMS-I2M: 2017-I2M-1-014/the CAMS Initiative for Innovative Medicine
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical