SPANX Control of Lamin A/C Modulates Nuclear Architecture and Promotes Melanoma Growth
- PMID: 32571981
- PMCID: PMC7541784
- DOI: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-20-0291
SPANX Control of Lamin A/C Modulates Nuclear Architecture and Promotes Melanoma Growth
Abstract
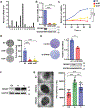
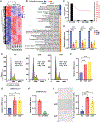
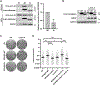
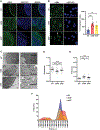
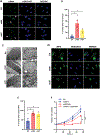
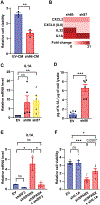
Mechanisms regulating nuclear organization control fundamental cellular processes, including the cell and chromatin organization. Their disorganization, including aberrant nuclear architecture, has been often implicated in cellular transformation. Here, we identify Lamin A, among proteins essential for nuclear architecture, as SPANX (sperm protein associated with the nucleus on the X chromosome), a cancer testis antigen previously linked to invasive tumor phenotypes, interacting protein in melanoma. SPANX interaction with Lamin A was mapped to the immunoglobulin fold-like domain, a region critical for Lamin A function, which is often mutated in laminopathies. SPANX downregulation in melanoma cell lines perturbed nuclear organization, decreased cell viability, and promoted senescence-associated phenotypes. Moreover, SPANX knockdown (KD) in melanoma cells promoted proliferation arrest, a phenotype mediated in part by IRF3/IL1A signaling. SPANX KD in melanoma cells also prompted the secretion of IL1A, which attenuated the proliferation of naïve melanoma cells. Identification of SPANX as a nuclear architecture complex component provides an unexpected insight into the regulation of Lamin A and its importance in melanoma. IMPLICATIONS: SPANX, a testis protein, interacts with LMNA and controls nuclear architecture and melanoma growth.
©2020 American Association for Cancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

