A new safety index based on intrapulse monitoring of ultra-harmonic cavitation during ultrasound-induced blood-brain barrier opening procedures
- PMID: 32572103
- PMCID: PMC7308405
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-020-66994-8
A new safety index based on intrapulse monitoring of ultra-harmonic cavitation during ultrasound-induced blood-brain barrier opening procedures
Abstract
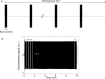
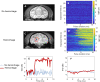
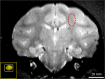
Ultrasound-induced blood-brain barrier (BBB) opening using microbubbles is a promising technique for local delivery of therapeutic molecules into the brain. The real-time control of the ultrasound dose delivered through the skull is necessary as the range of pressure for efficient and safe BBB opening is very narrow. Passive cavitation detection (PCD) is a method proposed to monitor the microbubble activity during ultrasound exposure. However, there is still no consensus on a reliable safety indicator able to predict potential damage in the brain. Current approaches for the control of the beam intensity based on PCD employ a full-pulse analysis and may suffer from a lack of sensitivity and poor reaction time. To overcome these limitations, we propose an intra-pulse analysis to monitor the evolution of the frequency content during ultrasound bursts. We hypothesized that the destabilization of microbubbles exposed to a critical level of ultrasound would result in the instantaneous generation of subharmonic and ultra-harmonic components. This specific signature was exploited to define a new sensitive indicator of the safety of the ultrasound protocol. The approach was validated in vivo in rats and non-human primates using a retrospective analysis. Our results demonstrate that intra-pulse monitoring was able to exhibit a sudden appearance of ultra-harmonics during the ultrasound excitation pulse. The repeated detection of such a signature within the excitation pulse was highly correlated with the occurrence of side effects such as hemorrhage and edema. Keeping the acoustic pressure at levels where no such sign of microbubble destabilization occurred resulted in safe BBB openings, as shown by MR images and gross pathology. This new indicator should be more sensitive than conventional full-pulse analysis and can be used to distinguish between potentially harmful and safe ultrasound conditions in the brain with very short reaction time.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Feedback control of microbubble cavitation for ultrasound-mediated blood-brain barrier disruption in non-human primates under magnetic resonance guidance.J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2019 Jul;39(7):1191-1203. doi: 10.1177/0271678X17753514. Epub 2018 Jan 30. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2019. PMID: 29381130 Free PMC article.
-
Focused ultrasound-mediated noninvasive blood-brain barrier modulation: preclinical examination of efficacy and safety in various sonication parameters.Neurosurg Focus. 2018 Feb;44(2):E15. doi: 10.3171/2017.11.FOCUS17627. Neurosurg Focus. 2018. PMID: 29385915
-
Acoustic cavitation-based monitoring of the reversibility and permeability of ultrasound-induced blood-brain barrier opening.Phys Med Biol. 2015 Dec 7;60(23):9079-94. doi: 10.1088/0031-9155/60/23/9079. Epub 2015 Nov 12. Phys Med Biol. 2015. PMID: 26562661 Free PMC article.
-
Ultrasound, microbubbles and the blood-brain barrier.Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2007 Jan-Apr;93(1-3):354-62. doi: 10.1016/j.pbiomolbio.2006.07.019. Epub 2006 Aug 4. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2007. PMID: 16959303 Review.
-
Ultrasound-induced blood-brain barrier opening.Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2012 Jun;13(7):1332-45. doi: 10.2174/138920112800624364. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2012. PMID: 22201586 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Guiding and monitoring focused ultrasound mediated blood-brain barrier opening in rats using power Doppler imaging and passive acoustic mapping.Sci Rep. 2022 Aug 30;12(1):14758. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-18328-z. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 36042266 Free PMC article.
-
FUS-mediated BBB opening leads to transient perfusion decrease and inflammation without acute or chronic brain lesion.Theranostics. 2024 Jul 2;14(10):4147-4160. doi: 10.7150/thno.96721. eCollection 2024. Theranostics. 2024. PMID: 38994025 Free PMC article.
-
Focused ultrasound-microbubble treatment arrests the growth and formation of cerebral cavernous malformations.Nat Biomed Eng. 2025 May 13:10.1038/s41551-025-01390-z. doi: 10.1038/s41551-025-01390-z. Online ahead of print. Nat Biomed Eng. 2025. PMID: 40360762 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Gambogic Acid-Loaded Porous-Lipid/PLGA Microbubbles in Combination With Ultrasound-Triggered Microbubble Destruction on Human Glioma.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2021 Sep 15;9:711787. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2021.711787. eCollection 2021. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2021. PMID: 34604184 Free PMC article.
-
Blood-brain barrier opening in a large animal model using closed-loop microbubble cavitation-based feedback control of focused ultrasound sonication.Sci Rep. 2022 Sep 27;12(1):16147. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-20568-y. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 36167747 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

